
“
Workplace ergonomics and back pain prevention are essential for ensuring comfort and productivity at work. A few small changes to your workspace and habits can go a long way in minimizing discomfort and improving overall health. Implementing proper ergonomic practices can help prevent back pain and create a healthier working environment. 1
1
”
Adjusting your workstation to support a neutral posture can reduce back pain. Adjust your chair, desk, and monitor height to keep your spine aligned and avoid strain during long periods of sitting. 1
Sitting for long periods can cause back pain. Taking regular breaks to stand, stretch, or walk helps relieve pressure on the spine, promoting better circulation and reducing stiffness in the lower back.2
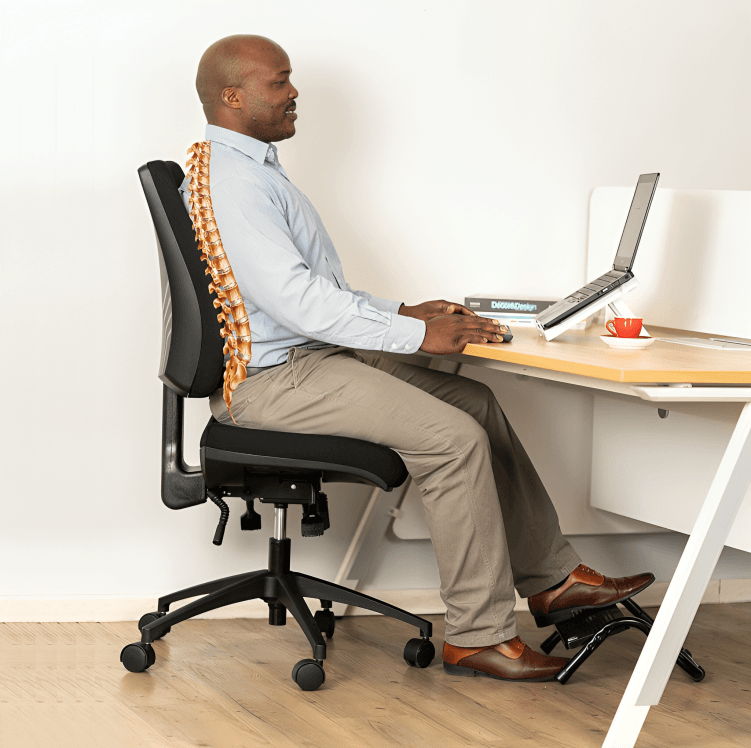

A chair with proper lumbar support prevents back pain by supporting the lower spine’s natural curve. This reduces muscle fatigue and strain during long sitting sessions, promoting better posture and comfort.
Keep your feet flat on the floor, with knees at a 90-degree angle when sitting. This posture helps align the spine and reduces strain, promoting healthier back alignment and preventing lower back discomfort.3
The top of your computer screen should be at eye level. This helps keep your neck in a neutral position, preventing strain in the neck, shoulders, and upper back, which can lead to discomfort over time.4
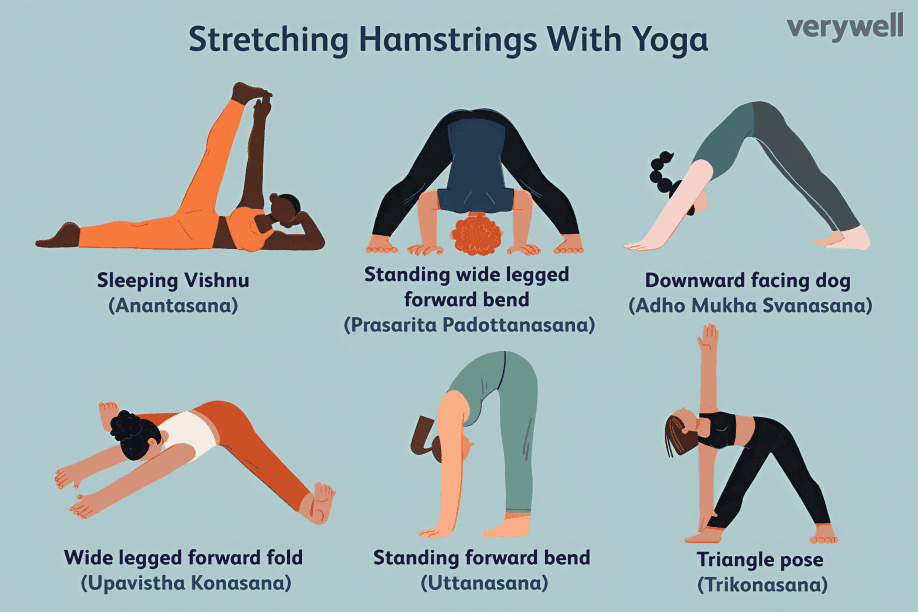
Regular stretching for the hamstrings, hip flexors, and lower back can help reduce muscle tightness and improve flexibility. This is crucial for maintaining good posture and preventing back pain from muscle stiffness.
Ensure your keyboard and mouse are at a comfortable height. Your forearms should be parallel to the floor when typing, reducing shoulder and back strain and preventing repetitive stress injuries. 5
Alternate between sitting and standing throughout the day. A sit-stand desk can provide flexibility, reducing the risk of back pain caused by staying in one position for extended periods. 6
Rest your arms comfortably at your sides to maintain a neutral posture. Avoid reaching forward or overextending, as this can cause muscle strain and contribute to back discomfort.7
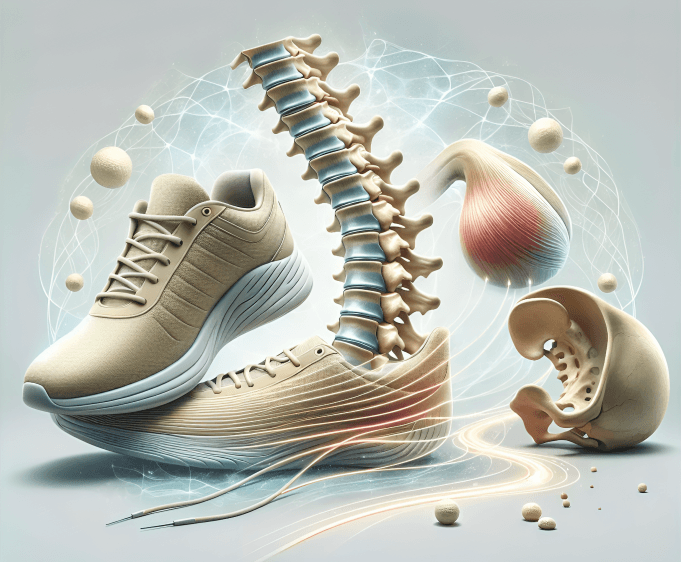

Wear supportive shoes with cushioning and proper arch support to reduce lower back strain. Good footwear can improve posture and help align your spine, reducing the risk of back pain during long hours of standing.
Strengthening your core muscles is essential for back pain prevention. A strong core stabilizes the spine and supports proper posture, reducing the likelihood of muscle fatigue and discomfort. 8
Using ergonomic accessories like footrests can help improve your sitting posture by aligning your legs properly and reducing strain on the lower back, promoting better spinal alignment.9
Lift objects using your legs, not your back. Bend at the knees, engage your core, and keep your back straight when lifting to avoid excessive pressure on your spine and reduce the risk of injury.10
A supportive mattress is essential for preventing back pain. Choose a mattress that supports spinal alignment, reduces pressure points, and helps you wake up without discomfort.11
Light physical activity like walking or swimming can improve back health. These exercises strengthen muscles around the spine, reducing the risk of back pain from weak or tight muscles. 12

Poor posture, such as slouching, leads to back pain. Maintaining an upright posture with your shoulders back and your head aligned with your spine helps prevent unnecessary strain on your back.
Stress can cause muscle tension, especially in the back. Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or yoga can reduce stress, helping to alleviate back pain caused by muscle tightness. 13
Keep frequently used items within reach to prevent stretching or twisting, which can strain your back. A well-organized workspace promotes healthy posture and reduces the risk of back discomfort. 14
If back pain persists, consult a healthcare provider. A physical therapist or chiropractor can recommend ergonomic adjustments and exercises to strengthen muscles and improve posture. 15
Maintain a neutral spine while sitting. Ensure your back is well-supported by your chair and that your head is aligned with your spine to prevent slouching, which can lead to back discomfort.16


