
“
The importance of breastfeeding for infant health has been emphasized by doctors and researchers worldwide. Breast milk is more than nutrition—it’s nature’s perfect formula that protects, nourishes, and strengthens a baby’s body and brain. From enhancing immunity to improving emotional bonding between mother and child, breastfeeding lays the foundation for lifelong wellness. 1
1
”
Dr. William Cadogan, a pioneer in pediatric care, advocated breastfeeding in the 18th century, emphasizing that natural feeding supports better digestion and healthier infant development than artificial substitutes 1
Breast milk contains live antibodies and white blood cells that protect infants against common infections such as diarrhea and ear infections, forming a shield around a baby’s immature immune system. 2
Colostrum, the thick yellowish milk produced right after birth, is rich in protein, low in fat, and packed with antibodies that act like the newborn's first vaccine by protecting from harmful pathogens.
Breastfeeding promotes a baby's brain development through nutrients like DHA, an omega-3 fatty acid critical for cognitive function, memory skills, and overall intelligence, as shown in developmental studies. 3
Exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months significantly reduces the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), as it supports better sleep patterns and stabilizes breathing and heart rate in infants. 4
Babies who are breastfed have a reduced risk of developing asthma and allergies later in life, thanks to the immune-regulating agents found naturally in human milk that help manage inflammatory responses. 5
Breastfeeding helps build a healthy gut microbiome, which influences not only digestion but also mental health, immunity, and chronic disease prevention as a child matures. 6
Breastfeeding protects infants from developing type 1 and type 2 diabetes by controlling early weight gain and offering hormones that help regulate blood sugar and insulin sensitivity from the start. 7
The act of suckling strengthens an infant’s jaw and facial muscles, supporting better speech development, oral health, and correct dental alignment during childhood and adolescence. 8

Studies show that breastfed children have lower chances of becoming obese later in life, as breastfeeding teaches them better self-regulation of appetite and lowers insulin-producing hormone levels.
Breastfed babies often score higher on intelligence tests and perform better academically, thanks to better mother-infant bonding and brain-boosting nutrients like choline and taurine. 9
The skin-to-skin contact during breastfeeding regulates a newborn's body temperature, heart rate, and stress hormones, promoting comfort, calmness, and a stronger emotional bond with the mother. 10
Breastfeeding is easily digestible, leading to fewer instances of constipation and colic in infants, contributing to better sleep cycles and general happiness in the first crucial months. 11
Long-term studies suggest that breastfed children are less likely to suffer from behavioral disorders, as early breastfeeding enhances emotional security and balanced neurochemical responses. 12
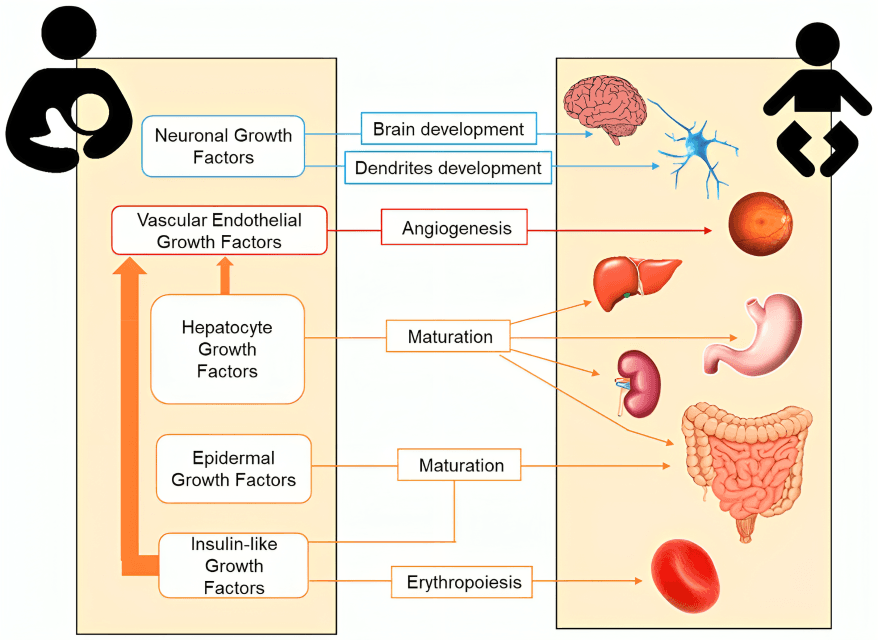
Breast milk includes enzymes and hormones that assist in tissue development and cellular growth, contributing to better organ function and physical development during infancy and early childhood.
Breastfed infants have fewer hospitalizations during their first year of life, showing how protective and preventive breastfeeding is against both short-term illnesses and long-term health issues. 13
Breastfeeding reduces the risk of childhood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma by reinforcing immune defense mechanisms and minimizing exposure to potentially harmful synthetic substances. 14
The act of breastfeeding fosters eye contact and emotional bonding, enhancing a child’s social and emotional intelligence through early relationship-building experiences with the mother. 15
Philosophers like Jean-Jacques Rousseau promoted natural mothering practices, including breastfeeding, recognizing it as vital for healthy emotional and physical growth in early human development. 16
Pediatricians worldwide consistently recommend breastfeeding due to overwhelming scientific evidence proving its unmatched health benefits for infants, supporting the body and mind in their most formative phase. 17


