
“
Breathing exercises' health benefits are often underrated, yet these simple techniques offer powerful support for both mind and body. From ancient philosophies to modern medicine, focused breathing helps reduce anxiety, enhance concentration, and even balance your heart rate and immunity. 1
1
”
Ancient Greek physician Hippocrates believed proper breathing was key to balancing the body’s inner energy. Today, science confirms deep breathing helps lower blood pressure and calm the nervous system. 1
Practicing daily breathing exercises helps reduce cortisol, the stress hormone, which allows the brain to shift from a reactive fight-or-flight state into a calmer and more thoughtful mental condition. 2
Slow, diaphragmatic breathing increases oxygen flow to the brain and improves memory, attention span, and emotional stability by stimulating the parasympathetic nervous system—your body's built-in relaxation mode. 3
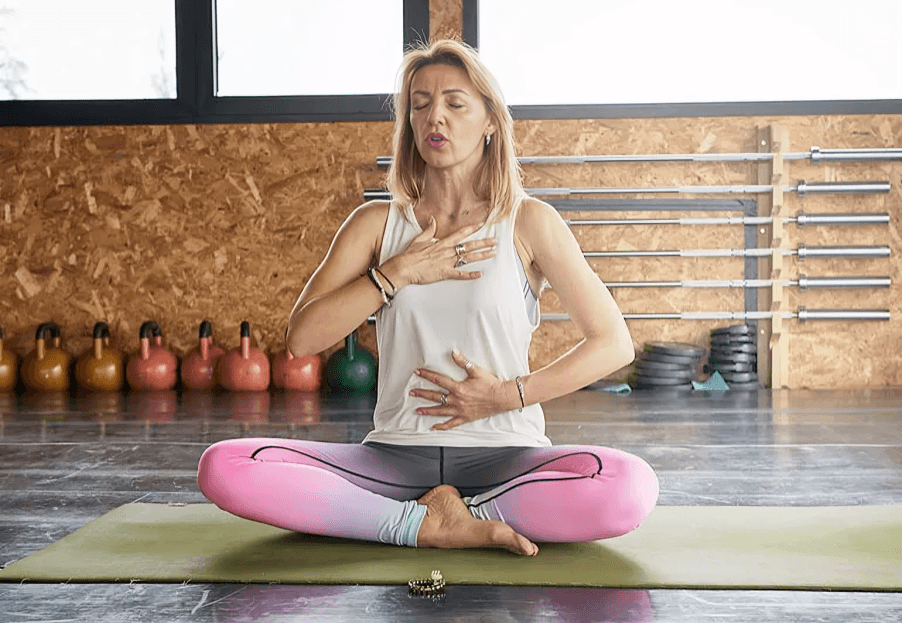

Focused breathing techniques, such as box breathing, help train the brain to remain calm in high-pressure moments, improving mental clarity, emotional resilience, and decision-making under stress.
Deep breathing activates the vagus nerve, which plays a central role in digestion, heart rate, and emotional regulation—supporting the connection between gut health and mental wellness. 4
Breathing exercises improve cardiovascular health by enhancing heart rate variability (HRV), which is a key biomarker for a resilient, adaptable, and healthy heart and emotional state. 5
When practiced regularly, slow breathing enhances lung capacity and oxygen efficiency, making daily tasks and physical exertion easier, especially for those with asthma, COPD, or shallow breathing patterns. 6
Rhythmic breathing has been shown to improve sleep quality by calming brainwave activity, easing muscle tension, and guiding the body into a restful state ideal for deep, uninterrupted rest. 7
Mindful breathing helps regulate blood glucose levels by reducing chronic stress, which has a significant influence on insulin resistance, inflammation, and the body’s ability to manage sugar intake. 8
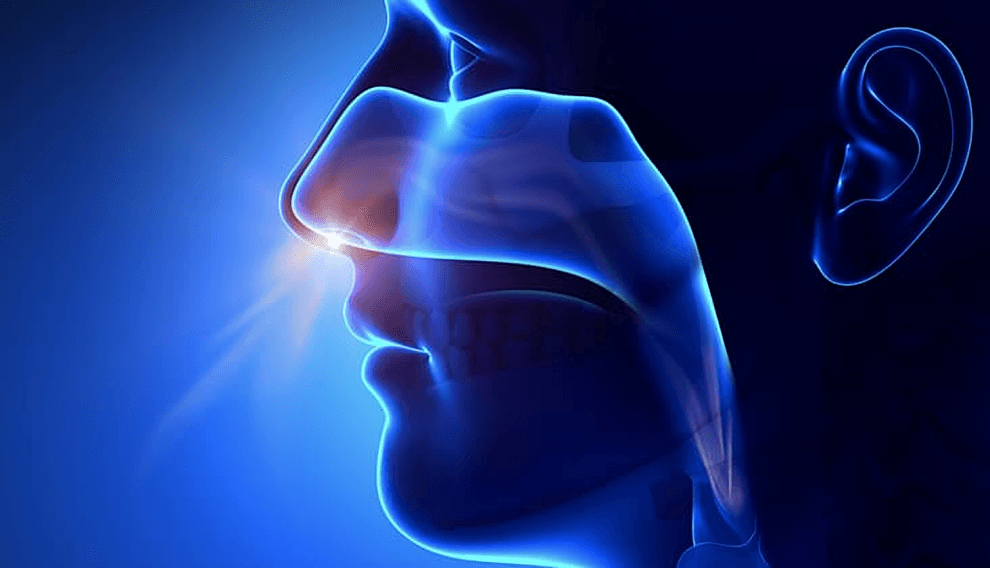
Inhaling slowly through the nose filters out airborne particles, warms the air, and promotes nitric oxide production, which opens blood vessels and improves circulation throughout the body.
Controlled breathing enhances focus and cognitive function by improving cerebral blood flow, helping people with ADHD, students, or anyone needing sharper attention and reduced mental fatigue. 9
Breath awareness practices like pranayama or coherent breathing increase mindfulness, helping people become more present and less overwhelmed by regrets of the past or fears of the future. 10
Intentional breathing increases oxygen saturation in the blood, improving cellular energy production and endurance for athletes, workers in high-demand fields, or individuals recovering from illness. 11
Breathing exercises reduce muscle tension by triggering a relaxation response that lowers adrenaline, creating physical ease and lessening symptoms of chronic pain or fatigue. 12
Studies have shown that breath regulation can lower heart rate in just minutes, offering a quick and reliable technique for calming the body during public speaking, exams, or emotional distress. 13
Coherent breathing practiced at a rhythm of five to six breaths per minute helps synchronize the body’s internal rhythms, improving both emotional balance and physical recovery from exertion. 14
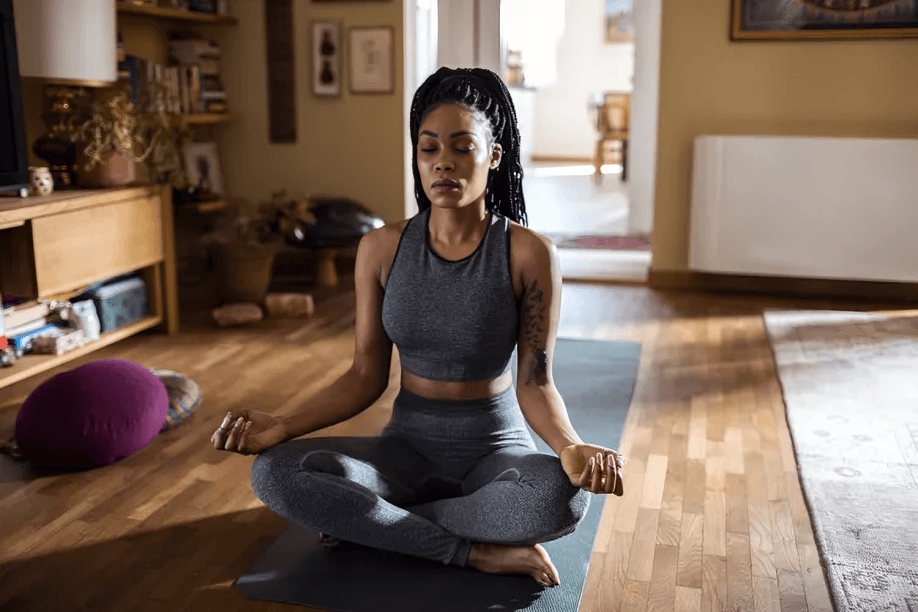

Breathing exercises act as a natural anti-anxiety tool by decreasing activity in the amygdala, the brain’s emotional center, and increasing prefrontal cortex function tied to calm reasoning.
Focused exhalation activates the parasympathetic system more deeply than inhalation, helping the body release tension, slow the heart, and signal that it's safe to relax and heal. 15
Breath control gives a sense of inner mastery and grounding, helping individuals develop resilience, especially during recovery from trauma, emotional setbacks, or overwhelming life transitions. 16
Ancient Chinese philosopher Lao Tzu described breath as the bridge between life and spirit. Today, therapists and doctors use breathing exercises to treat trauma and restore inner peace through body-mind integration. 17


