
“
Understanding the dangers of excess sugar consumption is crucial in today’s fast-paced world, where processed foods dominate diets. High sugar intake can silently impair organ function, fuel chronic disease, and negatively influence mental health. It’s not just about weight gain—its consequences are deeply woven into how our bodies operate daily. 1
1
”
Excess sugar consumption can disrupt hormone balance, leading to increased insulin resistance, which doctors warn is a primary factor in developing type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome over time. 1
According to medical experts, excess sugar promotes inflammation throughout the body, which contributes significantly to chronic diseases like arthritis, cardiovascular issues, and certain cancers. 2
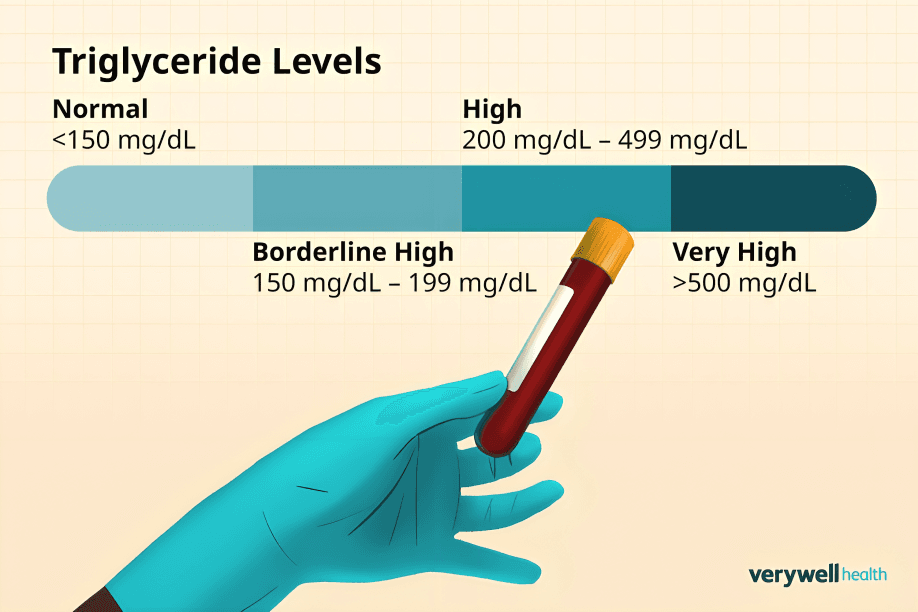
High sugar intake raises triglyceride levels in the blood, increasing the risk of heart disease by promoting artery clogging and affecting cholesterol balance negatively.
The brain’s reward system is hijacked by excessive sugar, leading to addictive eating behaviors that cause people to crave more sugary foods, often resulting in overeating and obesity. 3
Excess sugar consumption reduces the body’s ability to absorb important nutrients like calcium and magnesium, weakening bones and leading to osteoporosis risks. 4
Studies reveal that high sugar diets impair immune function, making the body more vulnerable to infections and slowing down recovery times from illnesses. 5
Elevated sugar intake is linked to increased anxiety and depression symptoms, as blood sugar spikes and crashes affect mood-regulating neurotransmitters in the brain. 6
Excess sugar often replaces healthier calories in the diet, reducing overall nutrient intake and contributing to malnutrition despite consuming high-energy foods. 7
Sugar-laden diets correlate strongly with the development of dental cavities and gum disease due to sugar feeding harmful bacteria that produce acid, eroding tooth enamel. 8
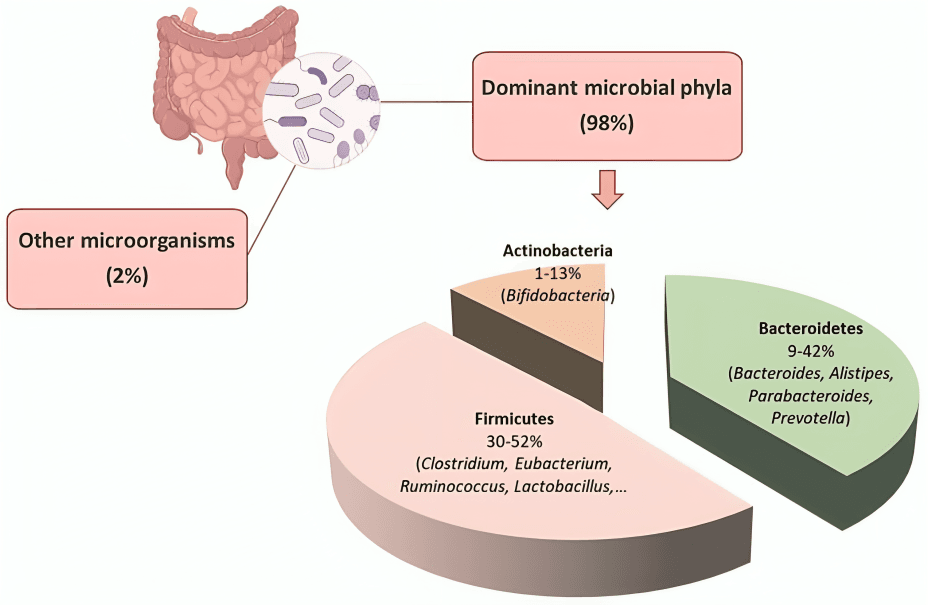
Consuming large amounts of sugar regularly disrupts gut microbiota balance, increasing harmful bacteria and inflammation, which can impair digestion and overall health.
Sugar causes rapid blood sugar spikes followed by crashes, which decrease energy levels and cognitive function, making concentration and memory tasks more difficult. 9
Excess sugar consumption has been linked to an increased risk of certain cancers, as chronic inflammation and insulin resistance create an environment conducive to tumor growth. 10
High sugar intake can exacerbate symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children, negatively affecting their behavior and learning capabilities. 11
Excessive sugar consumption can harm kidney function by increasing blood pressure and causing inflammation, which may lead to chronic kidney disease over time. 12
Sugar impacts cardiovascular health by increasing blood pressure, raising bad LDL cholesterol, and reducing good HDL cholesterol, which collectively increase heart disease risk. 13

Research shows that sugary beverages are a major contributor to obesity because they do not trigger the same fullness signals as solid foods, leading to excessive calorie intake.
Regular high sugar intake can lead to insulin resistance, a precursor to diabetes, making it difficult for the body to regulate blood sugar and leading to serious health complications. 14
Sugary foods often contribute to fatty deposits around internal organs, increasing the risk of metabolic syndrome, which is associated with heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. 15
Philosopher and physician René Dubos observed that excessive sugar disrupts the body’s natural balance and promotes disease, emphasizing the importance of natural diets for long-term health. 16
Modern doctors warn that reducing sugar intake is essential for preventing chronic illnesses, as the cumulative effects of excess sugar harm nearly every organ system in the body. 17


