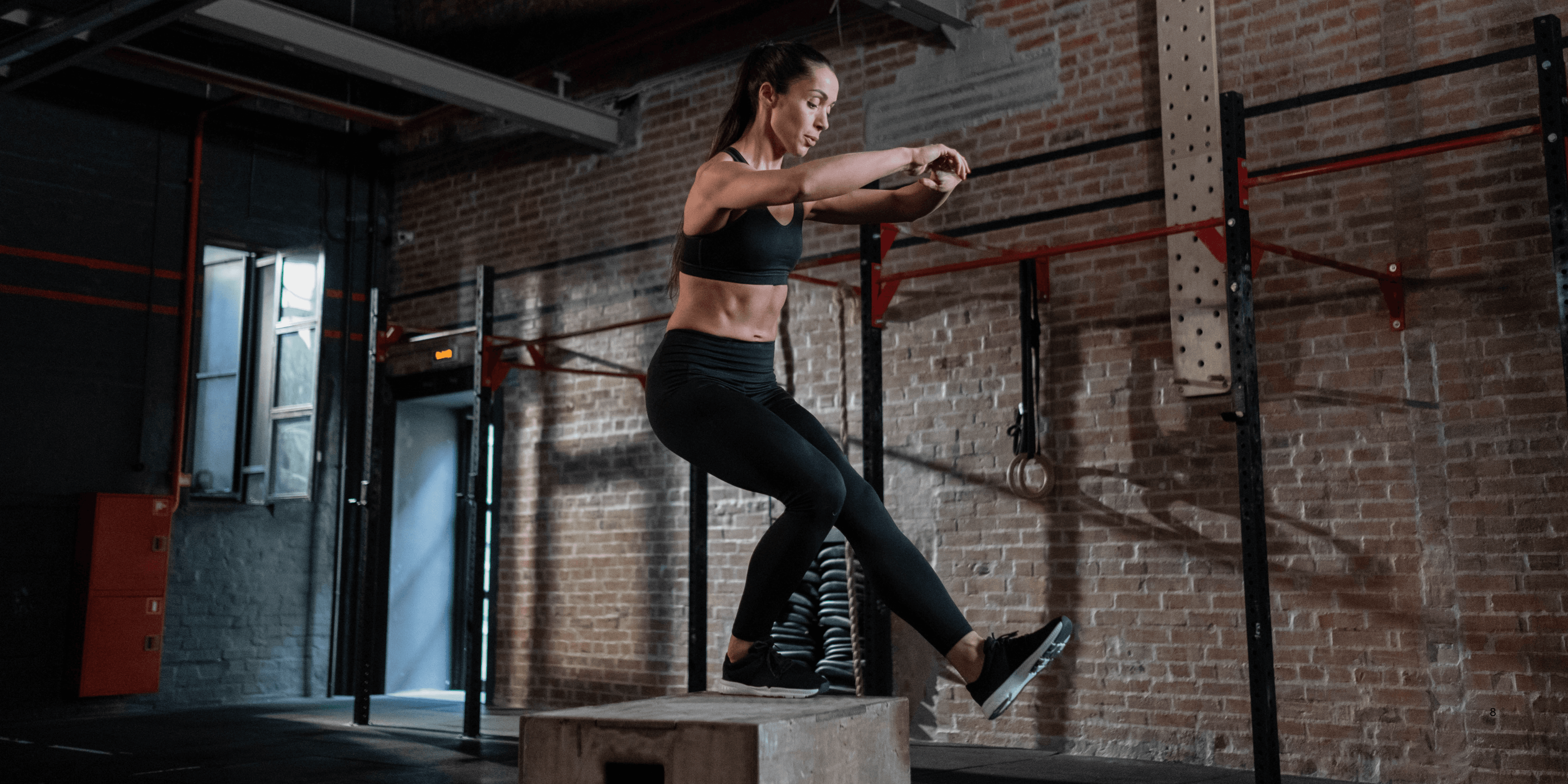

“
HIIT workouts: benefits and best practices have transformed fitness routines worldwide, offering an efficient way to burn fat, build endurance, and improve heart health. This method combines short bursts of intense activity with recovery periods, optimizing workout results in minimal time.1
1
”
Dr. Izumi Tabata, a Japanese scientist, developed a HIIT method using 20-second intense bursts, improving both aerobic and anaerobic fitness, transforming training for athletes and fitness enthusiasts. 1
HIIT workouts increase metabolism by elevating the afterburn effect, allowing your body to burn calories at a higher rate even hours after exercising, making fat loss more efficient than steady-state cardio. 2
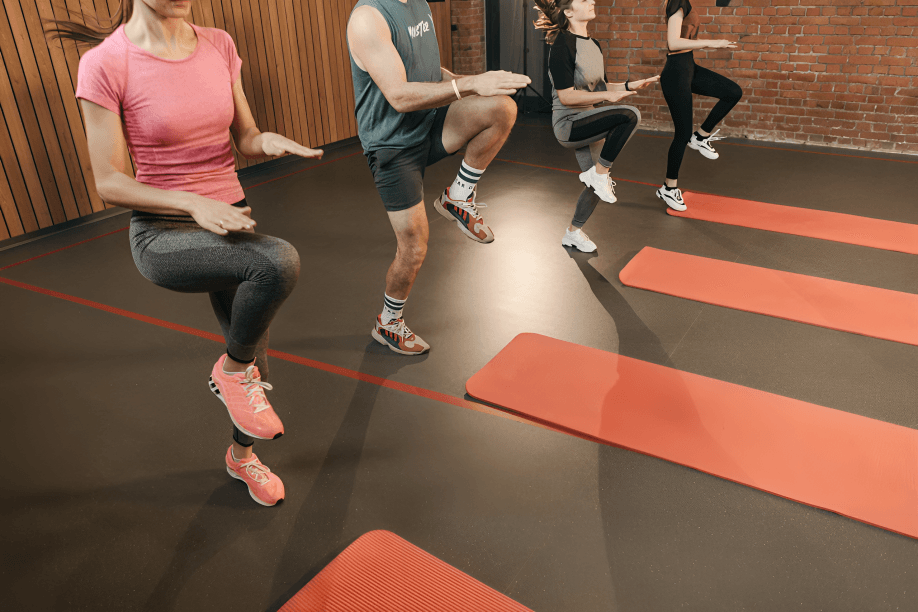

Short-duration HIIT sessions can improve cardiovascular fitness significantly, helping lower blood pressure and reducing the risk of heart disease more effectively than traditional moderate exercise routines.
HIIT training increases insulin sensitivity, which helps regulate blood sugar levels better, lowering the risk of type 2 diabetes and supporting overall metabolic health. 3
Unlike long cardio sessions, HIIT workouts preserve muscle mass while helping reduce fat, making them ideal for those wanting to stay lean and toned. 4
HIIT routines improve VO2 max, a key indicator of aerobic endurance, meaning your body becomes more efficient at using oxygen during intense physical activity. 5
One of the best practices in HIIT is to include a warm-up and cool-down to prevent injury and ensure muscles recover effectively after intense bursts of exercise. 6
HIIT can be adapted for all fitness levels by adjusting the intensity and duration of intervals, making it accessible whether you’re a beginner or an advanced athlete. 7
The high-intensity nature of HIIT stimulates the production of human growth hormone (HGH), which aids muscle repair, fat loss, and overall anti-aging effects. 8
Performing HIIT three times a week can improve aerobic and anaerobic performance while also increasing endurance without requiring long hours at the gym. 9
Incorporating variety in HIIT exercises, such as cycling, sprinting, or bodyweight movements, prevents boredom and keeps different muscle groups engaged for balanced fitness.
Studies show HIIT improves mental health by reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression, largely due to endorphin release and improved brain function. 10
HIIT workouts are effective for improving mitochondrial function in muscles, enhancing cellular energy production, which increases stamina and reduces fatigue. 11
A key benefit of HIIT is its ability to improve oxygen consumption efficiency, enabling your body to work harder and recover more quickly during and after workouts. 12
HIIT is time-efficient; even workouts lasting 15-20 minutes can deliver significant health and fitness benefits comparable to longer traditional exercise sessions. 13
Best practices suggest allowing 24-48 hours of recovery between HIIT sessions to enable muscle repair and avoid overtraining or injury. 14

Including strength training intervals in HIIT enhances muscle growth and strength, combining cardiovascular and resistance benefits in a single workout.
Regular HIIT can enhance cognitive function by boosting brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which supports learning, memory, and mental clarity. 15
Dr. John Ratey, a renowned psychiatrist, highlights how HIIT benefits brain health, improving mood, focus, and cognitive resilience through increased blood flow and neurogenesis. 16
Philosopher Friedrich Nietzsche emphasized the value of overcoming physical challenges, which aligns with HIIT’s intense nature, pushing individuals beyond their comfort zones for growth.17


