
“
Hormones in mood and mental stability play a vital role in shaping our emotional responses, stress reactions, and psychological well-being. These natural chemical messengers regulate brain activity, influencing how we think, feel, and react in different situations.1
1
”
Serotonin is a mood-stabilizing hormone made in the brain and gut. It helps regulate mood, sleep, and appetite, directly influencing emotional stability and feelings of happiness or anxiety. 1
Cortisol, often called the "stress hormone," is released by the adrenal glands and can heighten alertness. However, too much cortisol disrupts mood balance and weakens mental stability under chronic stress. 2
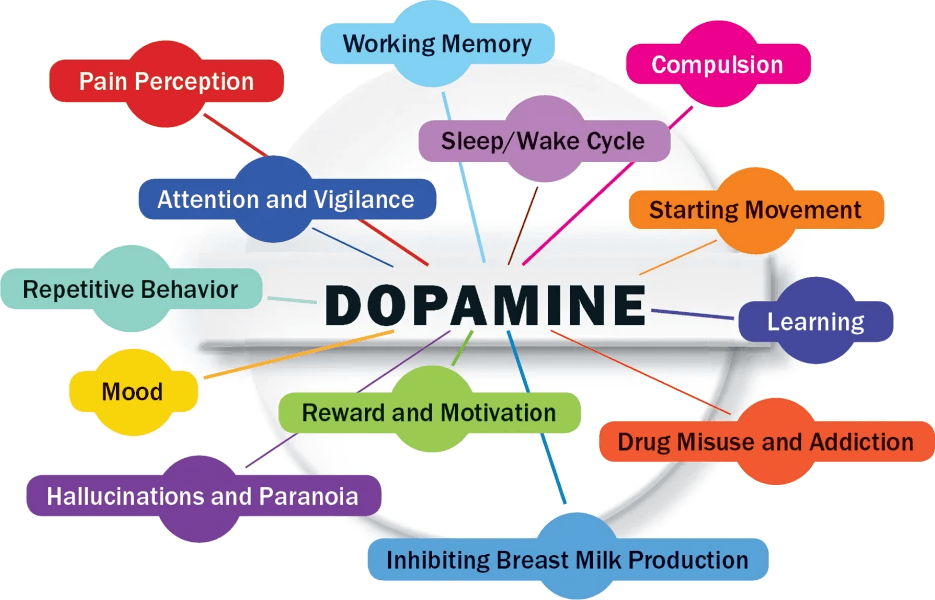
Dopamine is a reward-driven hormone that promotes motivation and pleasure. It drives our sense of achievement and goal-setting, and imbalances can lead to depression or compulsive behaviors like addiction.
Low levels of serotonin are linked to increased risk of anxiety disorders and depression. Antidepressants often target this hormone to stabilize emotional responses and prevent overwhelming sadness or irritability. 3
Oxytocin, the bonding hormone, plays a role in emotional connection and trust. It fosters feelings of love and safety, supporting mental balance in relationships and during nurturing experiences. 4
The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate energy and mood. An underactive thyroid can cause fatigue, low mood, and mental sluggishness, which affect both emotions and mental clarity. 5
Testosterone impacts mood regulation in both men and women. While often linked to aggression, it can also influence confidence, focus, and mental drive, depending on the hormone's balance in the body. 6
Estrogen interacts with brain chemicals like serotonin. Fluctuations in estrogen levels—especially during menopause—can cause mood swings, irritability, and emotional instability in many women. 7
Chronic stress elevates cortisol, which can shrink brain regions responsible for memory and emotional control. This hormonal imbalance increases vulnerability to anxiety, depression, and poor decision-making. 8
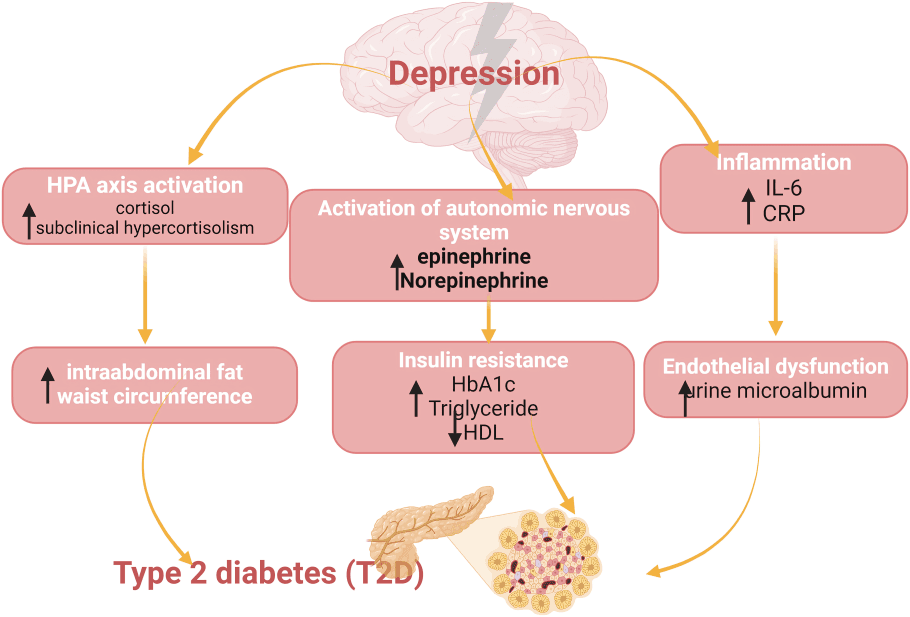
Insulin resistance, common in people with diabetes, disrupts blood sugar and may contribute to depression. Stable insulin levels support balanced brain function and overall mental resilience and clarity.
The gut-brain axis is influenced by hormones like serotonin, 90% of which is produced in the gut. This connection explains why digestive health impacts mental health and emotional reactions. 9
Adrenaline rushes during intense stress or fear trigger fight-or-flight responses. While short-term surges can help, chronic adrenaline imbalances lead to emotional instability and increased anxiety. 10
Melatonin not only regulates sleep but also contributes to emotional balance. Poor melatonin levels can disturb sleep patterns and leave the brain less equipped to manage mood swings and mental clarity. 11
Leptin, the hormone that regulates hunger, also affects emotions. Low leptin levels are associated with irritability and mood issues, especially in conditions like eating disorders or chronic dieting. 12
High cortisol levels affect serotonin receptors, making it harder for the brain to process happiness. This hormonal conflict can lead to emotional numbness or erratic mood changes over time. 13
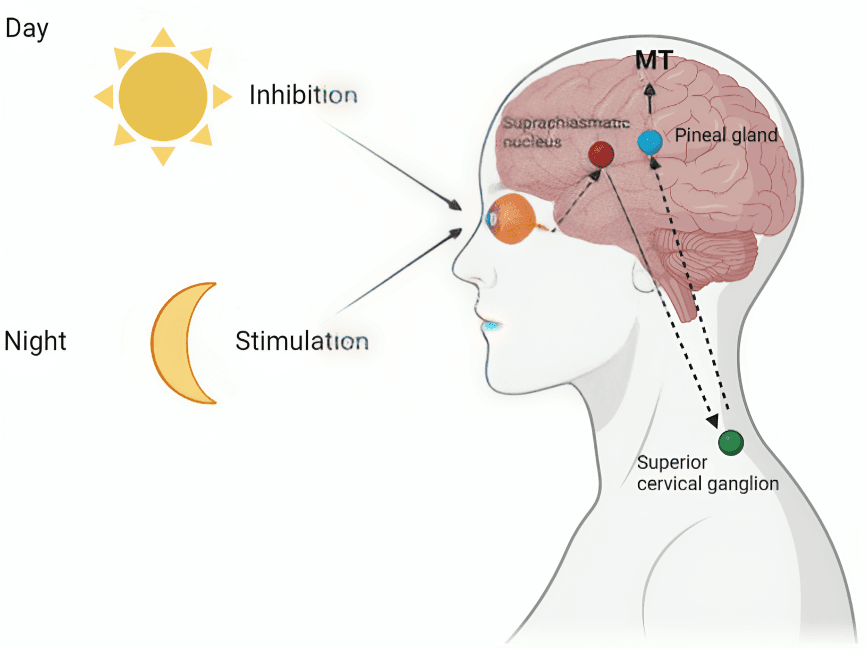
The pineal gland produces melatonin and interacts with emotional regulation. Disruption in its function can cause mood disorders, insomnia, and long-term mental instability if not managed well.
Neurotransmitters like GABA work with hormones to calm brain activity. When GABA is low, anxiety rises, showing how hormonal support systems are vital for relaxation and emotional control. 14
Hormonal contraceptives influence estrogen and progesterone levels. These changes can affect serotonin and mood, sometimes improving emotional balance or, in some cases, triggering sadness or anxiety. 15
Prolactin, mainly known for aiding lactation, also influences mood. Elevated prolactin levels are linked to emotional blunting and can disturb the natural rhythm of mental and emotional functioning. 16
Modern neurologists and psychologists agree that hormones in mood and mental stability are central to emotional wellness. Today's treatments combine therapy and hormone regulation for mood and mental stability. 17


