
“
How to Manage Osteoporosis isn’t just about preventing fractures—it's a lifelong journey of strengthening your bones, nourishing your body, and staying active with purpose. As bones gradually lose density, the risk of unexpected injuries increases. But there’s good news: how to manage osteoporosis is no longer a mystery locked in medical jargon or limited to calcium tablets.1
1
”
Engaging in regular weight-bearing and resistance exercises, such as walking, dancing, or lifting weights, stimulates bone formation and slows bone loss, thereby enhancing bone density. 1
Consuming a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is crucial for bone health; these nutrients work synergistically to strengthen bones and prevent deterioration associated with osteoporosis. 2
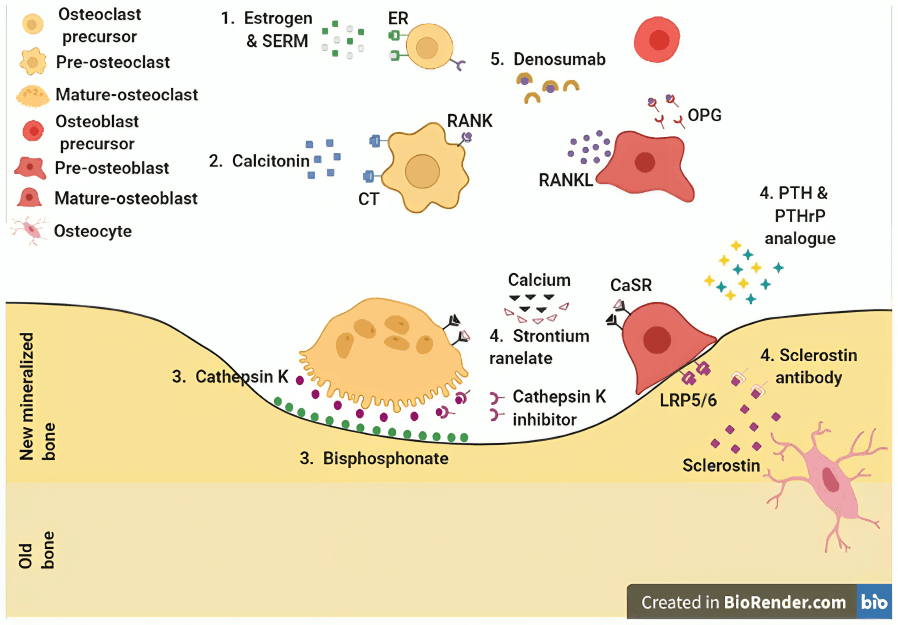
Bisphosphonates are commonly prescribed medications that slow bone loss by inhibiting osteoclast activity, thereby reducing fracture risk in individuals with osteoporosis.
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can be beneficial for postmenopausal women by maintaining estrogen levels, which helps preserve bone density and reduce fracture risk. 3
Regular bone density testing, such as dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scans, is essential for diagnosing osteoporosis and monitoring the effectiveness of treatment strategies. 4
Limiting alcohol intake and avoiding smoking are important lifestyle changes, as both can contribute to decreased bone density and increased fracture risk. 5

Incorporating balance and flexibility exercises, like tai chi or yoga, can improve coordination and reduce the risk of falls, which are a leading cause of fractures in individuals with osteoporosis.
Adequate protein intake supports bone health by providing the essential amino acids necessary for bone matrix formation and maintenance. 6
Monitoring and managing underlying health conditions, such as thyroid disorders or rheumatoid arthritis, is important, as these can affect bone metabolism and increase osteoporosis risk. 7
Ensuring sufficient magnesium and vitamin K intake supports bone health, as these nutrients play roles in bone mineralization and calcium regulation.8
Engaging in regular physical activity not only strengthens bones but also improves muscle strength, coordination, and balance, all of which contribute to reduced fracture risk. 9
Implementing home safety measures, like removing tripping hazards and installing grab bars, can reduce the risk of falls and fractures. Ensuring adequate lighting and using non-slip mats are also effective strategies. 10
Regular dental check-ups are vital, as osteoporosis drugs can harm the jawbone. Good oral hygiene and telling your dentist about medications help prevent complications like osteonecrosis.11
Monitoring bone turnover markers through blood or urine tests can provide insights into the effectiveness of osteoporosis treatments and disease progression. These markers help in individualized treatment plans. 12
Staying updated on new treatments and trials offers access to better osteoporosis therapies with fewer side effects. Discussing these options with healthcare providers is highly beneficial. 13
Implementing home safety measures—removing clutter, securing rugs, and installing grab bars in bathrooms and stairways—significantly reduces fall risk and helps prevent fractures.14
Regular dental check-ups are crucial, especially for those taking bisphosphonates, as these drugs may affect jawbone health and increase the risk of rare conditions like osteonecrosis of the jaw.15
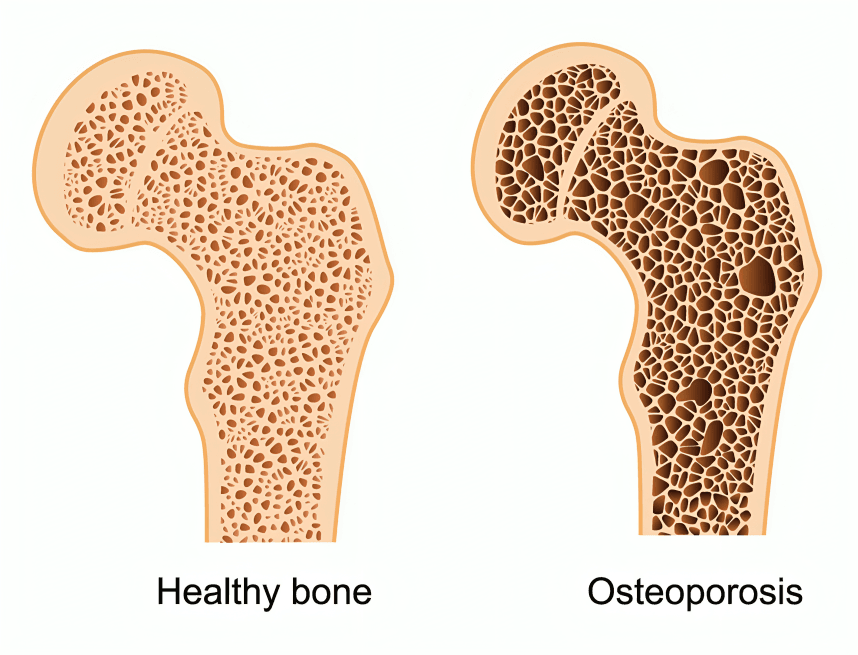
Monitoring bone turnover markers through blood or urine tests shows how quickly bone is broken down and rebuilt, offering insight into how well osteoporosis treatments are working and if adjustments are needed.
Keeping up with new osteoporosis treatments helps patients and doctors find options with better bone protection, fewer side effects, or easier dosing than current therapies.16
Regularly reviewing and adjusting treatment plans with healthcare providers ensures that osteoporosis management strategies remain effective and aligned with current health status. 17


