“
Managing high blood pressure in older adults is essential for maintaining overall health, preventing heart disease, and ensuring a better quality of life in later years. As aging naturally stiffens blood vessels, controlling hypertension becomes even more vital. 1
1
”
Many physicians emphasize that lifestyle changes can be as effective as medication when managing high blood pressure in older adults, especially when combined with consistent health monitoring. 1
Reduced salt intake helps lower blood pressure by decreasing fluid retention in older adults. Limiting daily sodium to under 1,500 mg is often recommended for those with hypertension concerns. 2
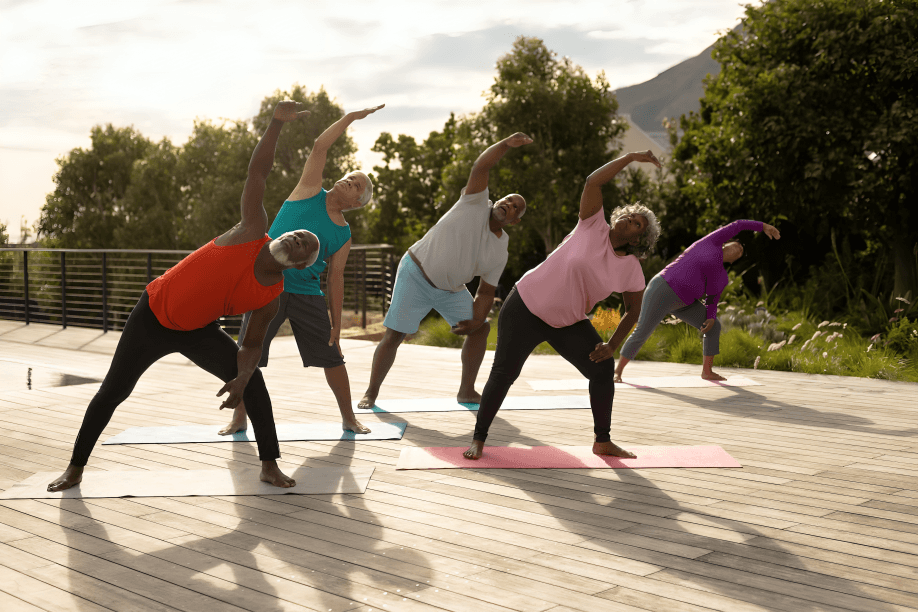
Regular physical activity, such as walking or light aerobics for 30 minutes daily, can significantly help older adults manage blood pressure and improve heart and vascular function naturally.
Eating a heart-healthy diet such as the DASH diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy, can effectively support lower blood pressure and reduce stroke risks in older people. 3
Stress contributes to blood pressure spikes, so older adults benefit from mindfulness techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or gentle yoga that promote relaxation and emotional stability. 4
Consistent sleep of 7–8 hours helps regulate blood pressure levels. Older adults with poor sleep patterns are more likely to develop resistant hypertension or other cardiovascular risks. 5
Cutting back on caffeine can stabilize blood pressure for older adults, especially for those sensitive to stimulants that trigger increased heart rate and vessel constriction. 6
Alcohol moderation is crucial. More than one daily drink may raise blood pressure and reduce medication effectiveness in elderly individuals managing hypertension. 7
Quitting smoking immediately benefits blood pressure. Nicotine narrows blood vessels, but quitting can improve circulation and reduce heart disease risks in older patients. 8
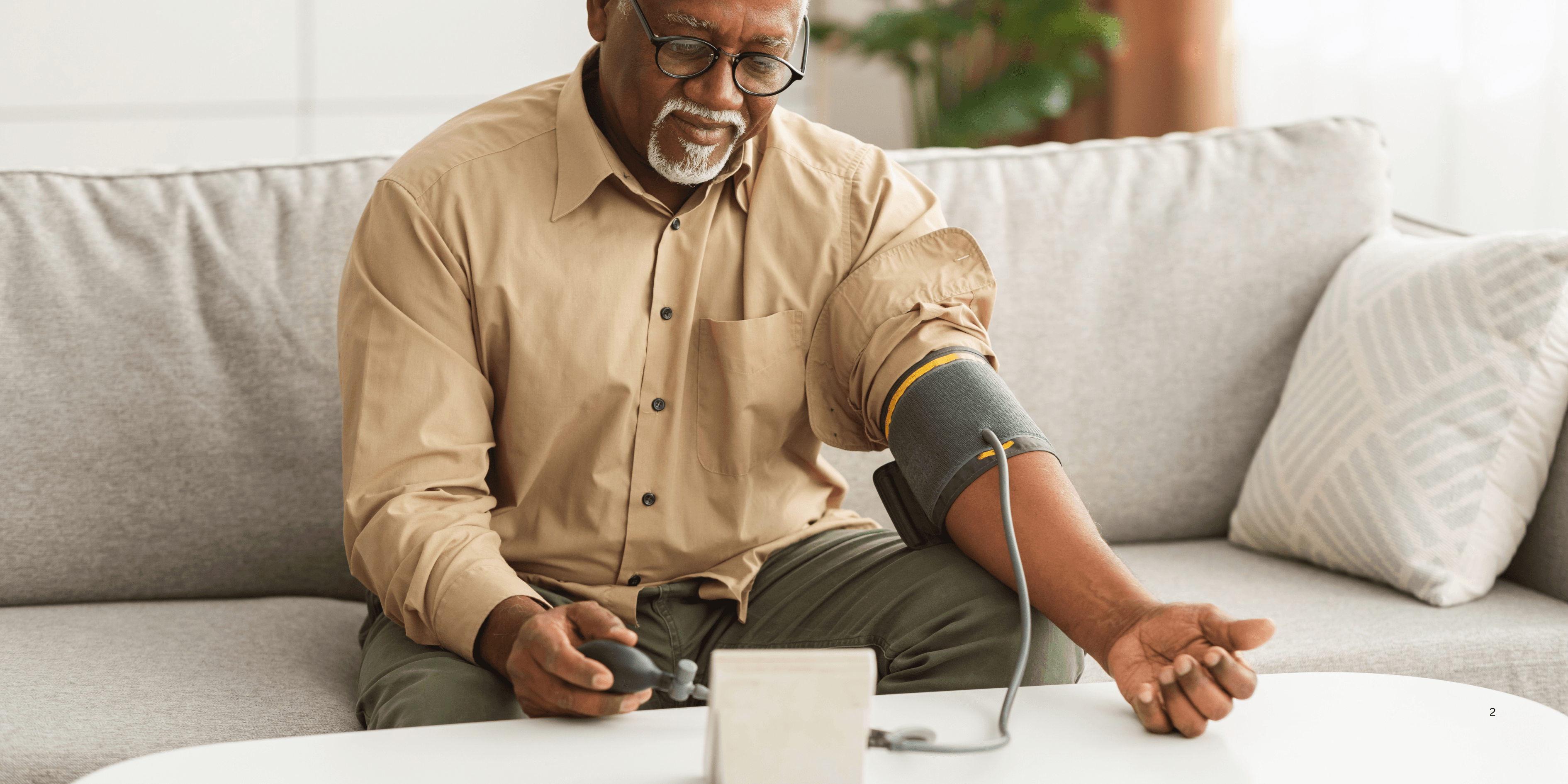
Regular blood pressure monitoring at home helps older adults catch fluctuations early. Keeping a log enables healthcare providers to adjust treatment or medications appropriately. 9
Weight loss, even a small amount like 5–10 pounds, significantly lowers blood pressure and eases strain on the heart and arteries for older individuals struggling with hypertension. 10
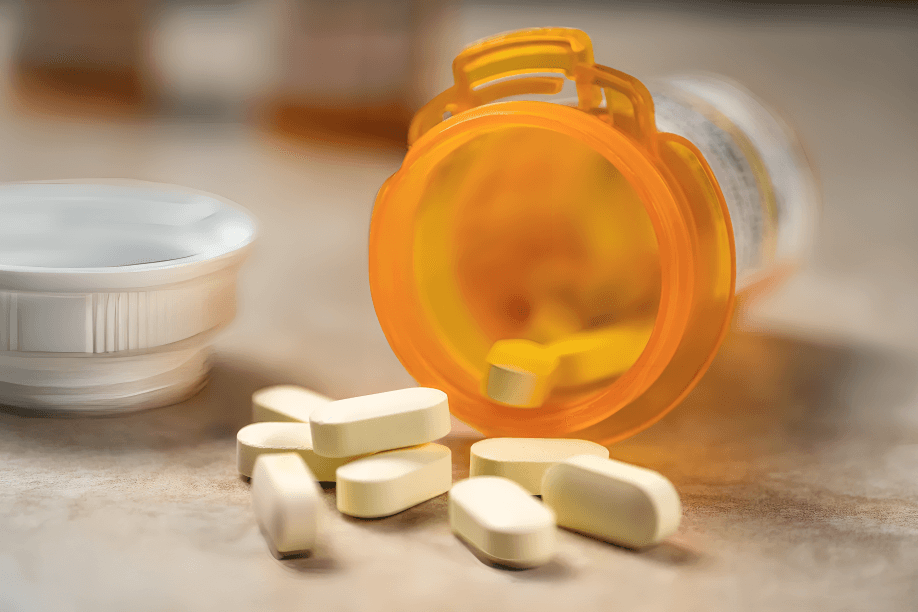
Diuretics are often prescribed to older adults with hypertension. These “water pills” help reduce fluid buildup and ease pressure on blood vessels, particularly in those with coexisting heart conditions.
Potassium-rich foods like bananas and sweet potatoes help counteract sodium’s effects and promote blood vessel flexibility in elderly people managing high blood pressure. 11
Proper hydration supports kidney function and blood circulation. Older adults sometimes drink less water, which can concentrate blood and raise blood pressure levels over time. 12
Limiting processed foods, which are high in hidden sodium and preservatives, helps maintain a more natural diet that’s beneficial for older adults with elevated blood pressure. 13
Some blood pressure medications may cause dizziness or lightheadedness in the elderly. Regular checkups help doctors adjust doses or change prescriptions to ensure safety. 14
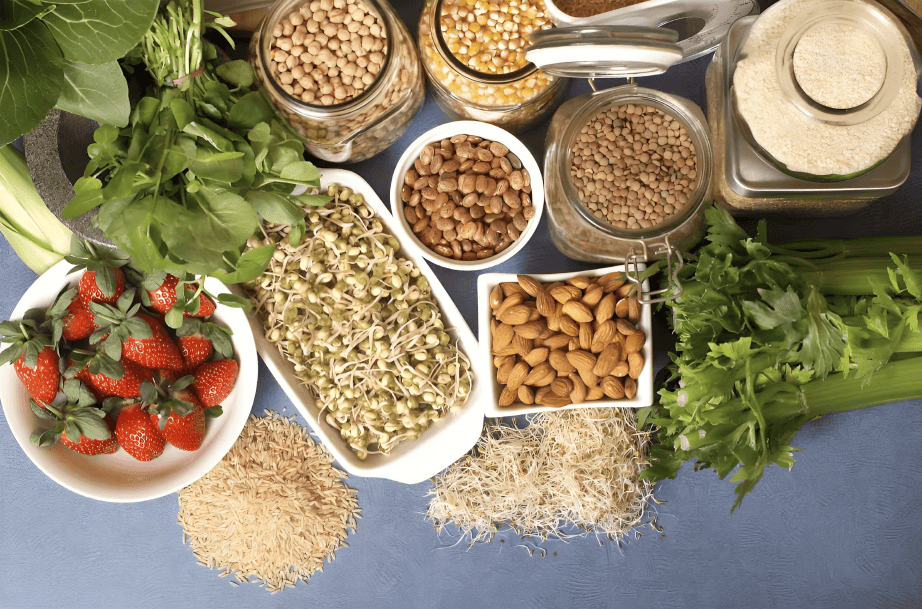

Fiber intake, through whole grains and legumes, can help reduce cholesterol and support better blood pressure control in older adults aiming for heart-friendly nutrition.
Omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish can reduce blood pressure and inflammation. Including salmon, mackerel, or flaxseeds helps promote vascular health in aging populations. 15
Regular eye exams are essential, as high blood pressure can cause damage to blood vessels in the eyes, leading to vision problems or even loss in elderly individuals. 16
Some doctors recommend integrating tai chi or other traditional movement-based practices into older adults’ routines to help regulate blood pressure and support a balanced lifestyle over time. 17


