
“
The science behind mindfulness shows how simple practices like meditation can profoundly affect the brain and body. Exploring the science behind mindfulness unveils how ancient techniques now influence modern medicine, psychology, and everyday stress management. In this article, we uncover the truth behind the science behind mindfulness through 20 fascinating, research-backed facts. 1
1
”
Mindfulness Meditation promotes neuroplasticity, allowing the brain to rewire itself by forming new connections. This increased flexibility boosts memory, creativity, and adaptability to changing life situations. 1
Scientific research reveals that regular meditation thickens gray matter in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus—brain areas crucial for learning and emotional balance—making the brain more resilient to stress. 2
When practicing mindfulness consistently, activity in the brain’s amygdala—the stress and fear center—significantly decreases, improving how people handle anxiety, and emotionally charged reactions in daily life. 3
Dr. Jon Kabat-Zinn, founder of Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR), pioneered clinical programs integrating mindfulness into healthcare. His work proved that mindfulness reduces anxiety, pain, and depression in patients. 4
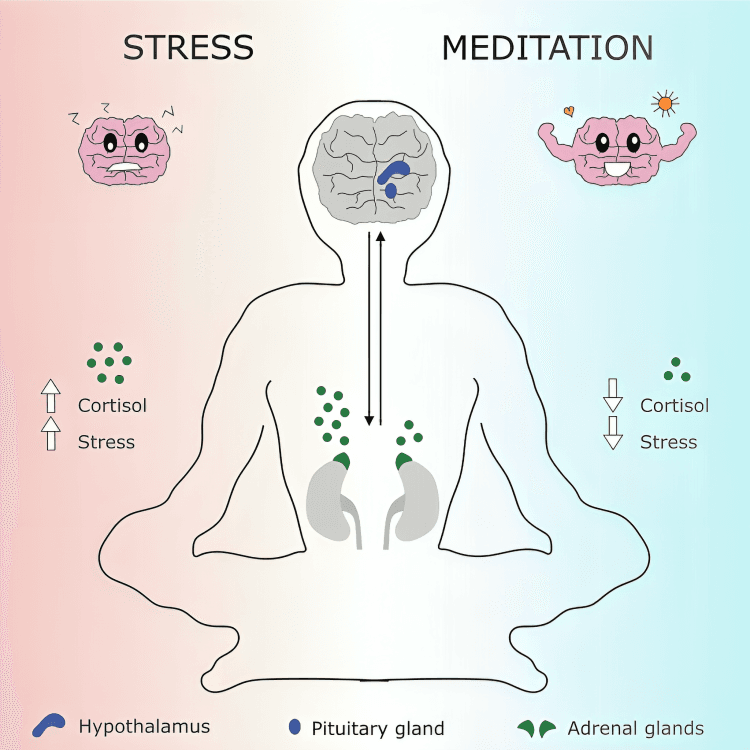
Meditation helps regulate the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, lowering cortisol—the body’s main stress hormone. This response reduces long-term stress and helps prevent conditions like hypertension and insomnia.
Practicing focused meditation strengthens the brain’s ability to sustain attention over time. It allows people to concentrate better, ignore distractions, and perform mentally demanding tasks with enhanced focus. 5
Meditation activates the parasympathetic nervous system, helping lower blood pressure by relaxing vessels and slowing the heart rate, offering a natural method for better cardiovascular health. 6
Mindfulness can strengthen the immune system function by reducing inflammation and increasing antibodies. It also boosts the body’s defenses against infections by calming the nervous system. 7
People who meditate regularly show fewer symptoms of depression due to changes in brain activity and increased release of serotonin and dopamine—neurotransmitters linked to positive emotions and motivation. 8
Through consistent practice, mindfulness alters the brain’s pain-processing areas. It helps people better tolerate chronic pain by easing the emotional intensity and mental suffering linked to physical discomfort. 9

Meditation preserves cognitive functions in older adults. It slows the natural decline of memory, focus, and mental agility, helping older individuals maintain independence, clarity, and quality of life.
Research shows mindfulness meditation helps manage PTSD symptoms by promoting inner awareness and emotional regulation, allowing individuals to respond to triggers more calmly and recover from trauma. 10
Practicing mindfulness reduces rumination—those repetitive, negative thought loops—by promoting present-moment awareness and detaching from unhelpful patterns. This rewiring leads to greater inner peace.11
For those in recovery, mindfulness enhances awareness of cravings and interrupts automatic addictive behaviors. It helps rebuild emotional resilience, self-control, and compassion toward oneself during the healing journey. 12
Ancient Greek philosopher Epictetus believed inner peace stems from mastering our thoughts, not external control. His Stoic teachings resonate with modern mindfulness and acceptance as paths to freedom. 13
Meditation fosters emotional stability by promoting alpha brainwave activity and increasing serotonin, making people feel happier and more emotionally balanced, even during stressful circumstances. 14
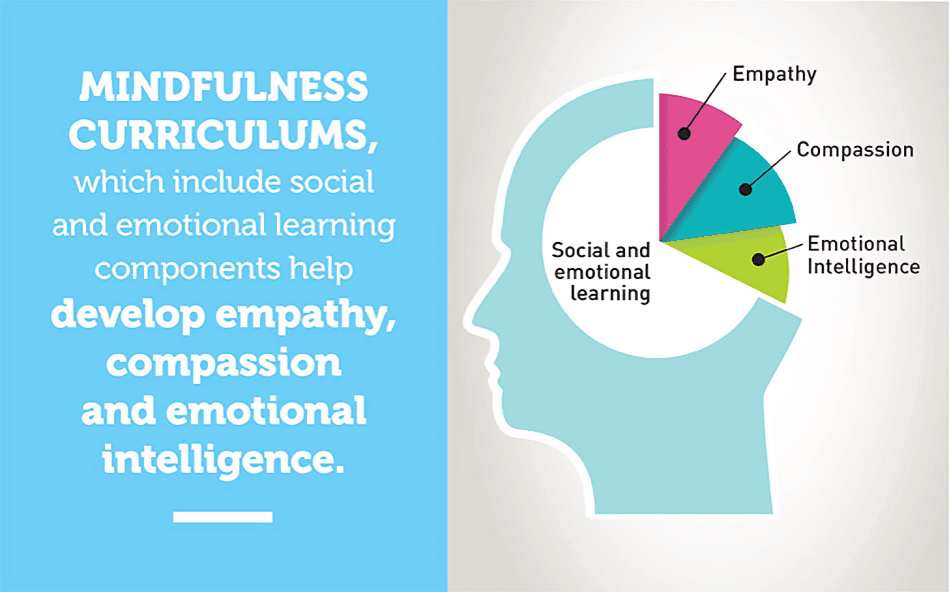
Mindfulness encourages empathy and compassion by activating brain regions involved in understanding others. This emotional intelligence helps people forge stronger, more meaningful relationships with family and friends.
During deep meditation, the brain generates theta waves—linked to creative insights and problem-solving—unlocking new ideas and approaches in personal and professional life without conscious effort. 15
Mindfulness improves eating habits by teaching people to savor each bite, recognize hunger cues, and reduce impulsive or emotional eating—supporting better weight management and digestive health. 16
A consistent meditation routine enhances creative thinking and innovation by calming mental noise. This allows the brain to form new ideas and connect seemingly unrelated concepts more fluidly. 17


