“
In today’s hyperconnected world, the effects of social media on mental health have become a growing concern. While digital platforms offer opportunities to connect and express, they also bring risks like anxiety, isolation, and low self-esteem. 1
1
”
Excessive social media use can lead to increased feelings of anxiety and depression. A University of Pennsylvania study found that using social media for only 30 minutes daily greatly reduced depression and loneliness. 1
"Snapchat dysmorphia" is a trend where people seek cosmetic surgery to look like their filtered selfies, highlighting social media's effect on body image and self-perception.2
Social media platforms often showcase idealized images and lifestyles, leading users to make unrealistic comparisons. This constant comparison can result in feelings of inadequacy and decreased self-esteem. 3

The blue light emitted by screens can interfere with melatonin production, disrupting sleep patterns. Using social media before bedtime has been linked to insomnia and poor sleep quality, which in turn affects mental health.
Social media addiction is characterized by compulsive use and an inability to control time spent online. This addiction can lead to significant impairments in daily functioning and mental well-being. 4
The constant stream of information on social media can lead to information overload, causing users to feel overwhelmed and anxious. This overload can impair decision-making and increase stress levels. 5
"Doomscrolling," or the compulsive consumption of negative news on social media, has been linked to increased anxiety and a decline in mental health. This behavior became particularly prevalent during the COVID-19 pandemic. 6
Social media platforms can perpetuate unrealistic beauty standards, leading to body dissatisfaction. Exposure to idealized images can negatively impact individuals' perceptions of their own bodies. 7
Social media platforms have become instrumental in spreading mental health awareness and reducing stigma. Campaigns and discussions online encourage individuals to seek help and share their experiences. 8
The curated nature of social media content can lead users to believe that others lead more successful or happier lives, fostering feelings of envy and inadequacy. This perception can negatively impact mental well-being. 9

Excessive social media use has been linked to decreased academic performance among students. The distraction and time spent online can interfere with study habits and concentration.
Social media can serve as a platform for individuals to express themselves and find validation, which can be beneficial for self-esteem. However, over-reliance on online validation can also lead to emotional dependency. 10
The fear of missing out (FOMO) is exacerbated by social media, where users constantly see updates about others' activities. This can lead to feelings of exclusion and decreased life satisfaction. 11
Social media use has been associated with increased levels of stress, particularly when users engage in arguments or are exposed to distressing content. This stress can have cumulative effects on mental health. 12
The anonymity of social media can lead to disinhibited behavior, where users say things they wouldn't in person. This can result in harmful interactions and increased online hostility. 13
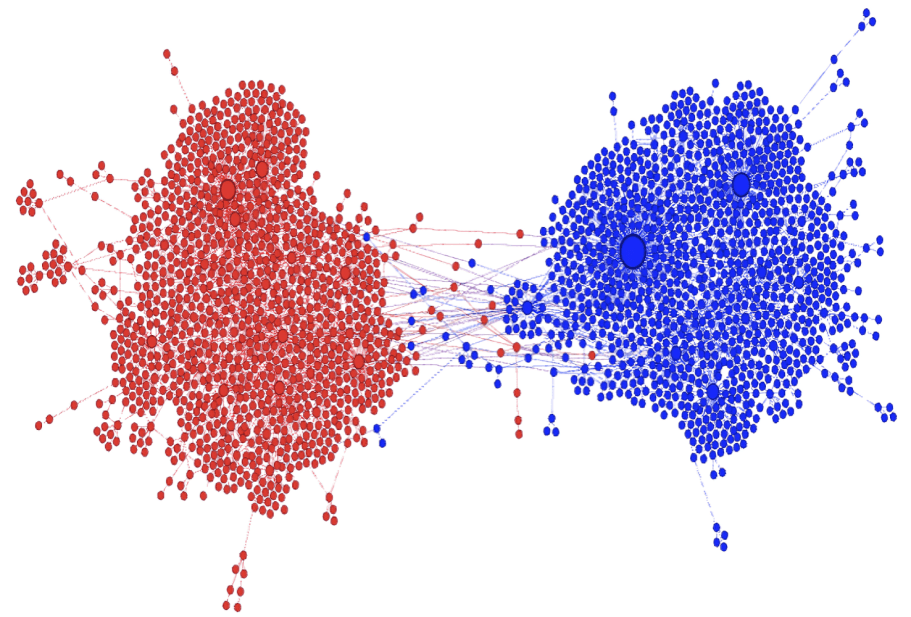
Social media platforms often use algorithms that reinforce users' existing beliefs, creating echo chambers. This can limit exposure to diverse perspectives and contribute to polarized thinking.
The pressure to maintain an online presence can lead to anxiety, especially when users feel compelled to post regularly or respond promptly to messages. This constant connectivity can be mentally exhausting. 14
Social media can impact self-worth, especially when users equate likes and comments with personal value. This external validation can become a significant factor in one's self-esteem. 15
Exposure to traumatic events or distressing news on social media can lead to secondary traumatic stress. Repeated exposure to such content can have lasting psychological effects. 16
Social media can disrupt real-life social interactions, with users spending more time online than engaging face-to-face. This shift can lead to feelings of isolation and decreased social skills. 17


