
“
Sugar & artificial sweeteners are everywhere in modern diets, but what’s the real truth about them? There’s a lot of confusion surrounding these ingredients, with many believing artificial sweeteners are a healthier alternative to regular sugar. However, the reality is much more complex. While sugar plays a significant role in adding taste and energy, artificial sweeteners often make an appearance in low-calorie and sugar-free products. But are they the better choice for health-conscious consumers? Read on for the essential facts about sugar & artificial sweeteners and their surprising effects. 1
”
Regular sugar consumption leads to an increase in blood glucose levels, which can be problematic for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. It's important to manage sugar intake for metabolic health.1
While artificial sweeteners provide a sweet taste with fewer calories, some studies suggest that they may trigger a craving for sweet foods, potentially leading to overeating and hindering weight loss efforts. 2
High consumption of refined sugars can increase the risk of developing cavities, as they feed the bacteria in the mouth that produce acids, damaging tooth enamel over time. Maintaining oral hygiene can mitigate this risk.3
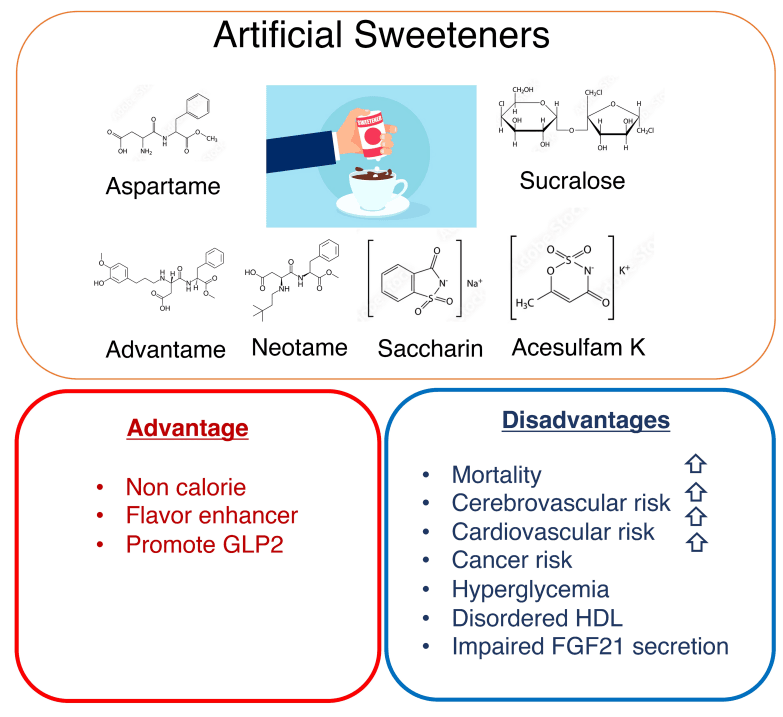
Artificial sweeteners like aspartame and sucralose are chemically different from sugar, but their use has raised questions regarding their safety. Regulatory bodies, including the FDA, have deemed them safe within recommended limits.
Sugar, when consumed in excessive amounts, can contribute to the accumulation of belly fat, which is linked to numerous health problems, including heart disease, high blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes.4
Artificial sweeteners, while lower in calories, may still trigger an insulin response in some individuals, making them unsuitable for people trying to control blood sugar levels.5
Excessive sugar intake is linked to chronic inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is believed to play a role in several diseases, including arthritis, heart disease, and even certain cancers. 6
Sugar contributes to the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which accelerate the aging process and damage tissues, including the skin. This can lead to wrinkles, making sugar reduction beneficial for skin health. 7

Studies have shown that while artificial sweeteners like stevia and erythritol are generally considered safe, excessive use may cause digestive discomfort, including bloating and gas. Moderation is key for avoiding these issues.
Unlike sugar, which provides a quick energy boost followed by a crash, artificial sweeteners do not raise blood glucose levels, making them a popular choice for people managing their energy levels or trying to lose weight.8
Despite their lack of calories, artificial sweeteners have been linked to potential metabolic disruptions. Some research suggests that these sweeteners might interfere with the body's ability to regulate blood sugar effectively.9
Although sugar is often blamed for weight gain, it is the overconsumption of calories from any source, whether natural or artificial—that leads to weight gain. Moderation in calorie intake is essential for maintaining a healthy weight.10

The sweetness of sugar comes from its ability to stimulate taste receptors, which can cause an overactive response in the brain, leading to an increased desire for more sweet foods. This reinforces the cycle of cravings.
While sugar is often considered an addictive substance due to its impact on the brain's reward system, artificial sweeteners do not cause the same level of addiction, although some individuals report craving sweet tastes.11
Long-term sugar intake is linked to increased triglyceride levels, which can contribute to cardiovascular problems, including atherosclerosis. Reducing sugar consumption can help lower these levels and improve heart health.12
Some sugar substitutes, like agave nectar, are marketed as healthier alternatives, but they can be just as high in fructose as high-fructose corn syrup, potentially leading to liver strain and insulin resistance. 13
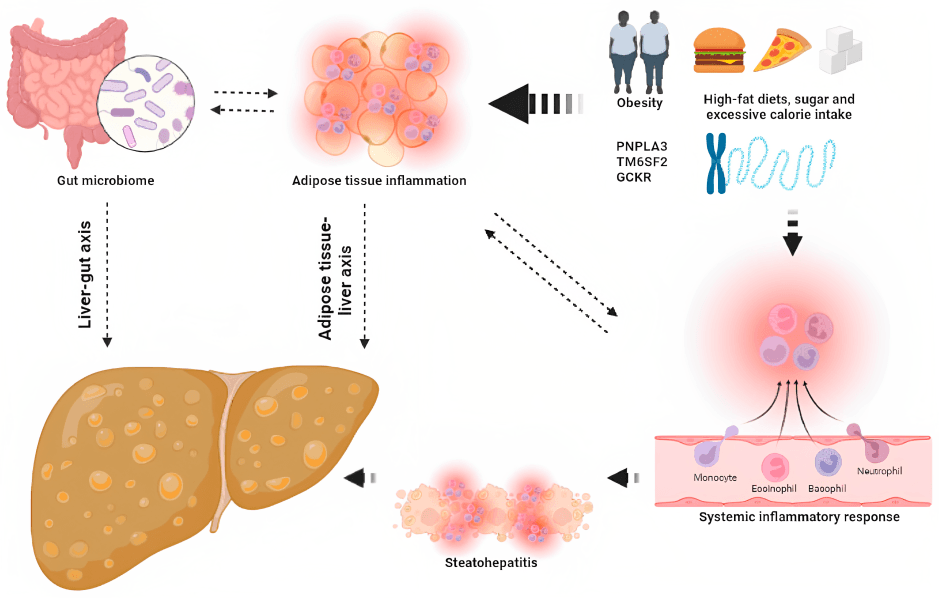
Regular sugar is metabolized by the liver, and excess intake can lead to fat storage in the liver, contributing to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Limiting sugar can support better liver function.
Although some individuals choose artificial sweeteners to avoid sugar’s negative health effects, studies suggest that switching to these substitutes without reducing overall calorie consumption may not lead to weight loss. 14
While sugar can contribute to the development of acne, especially in individuals with a sensitivity to insulin spikes, the connection between artificial sweeteners and skin health is still unclear.15
Artificial sweeteners have been suggested to alter the body's natural preference for healthy foods. People who regularly these may develop an increased desire for overly sweet foods and nutrient-dense options from their diet. 16


