“
Thyroid disorders and their impact on health are more common than many realize, and they can significantly affect one’s quality of life. The thyroid, a small butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy production, and overall body function. Any disruption in its function can lead to a variety of health issues, ranging from fatigue and weight gain to more severe conditions like heart disease and infertility. 1
”
Thyroid disorders are commonly categorized into hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Hypothyroidism causes fatigue and weight gain, while hyperthyroidism leads to weight loss and heart issues.1
A common sign of hypothyroidism is weight gain, as the body’s metabolism slows down due to lower levels of thyroid hormones, making it harder to lose weight or maintain a healthy body weight. 2
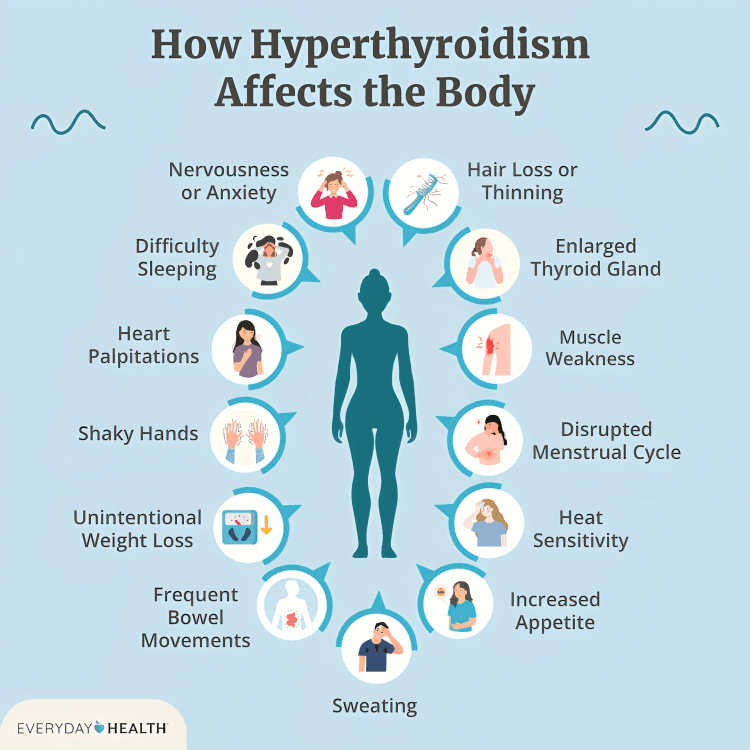
People with hyperthyroidism often experience symptoms like nervousness, rapid heartbeats, and increased sweating. It’s caused by excess thyroid hormones that speed up metabolism and heart rate.
Women face a higher risk of thyroid disorders, especially during and after pregnancy. Postpartum thyroiditis may cause hormone fluctuations that negatively affect overall health. 3
Untreated thyroid issues can harm the heart. Hypothyroidism raises cholesterol and heart disease risk, while hyperthyroidism may cause arrhythmias, heart failure, or stroke. 4
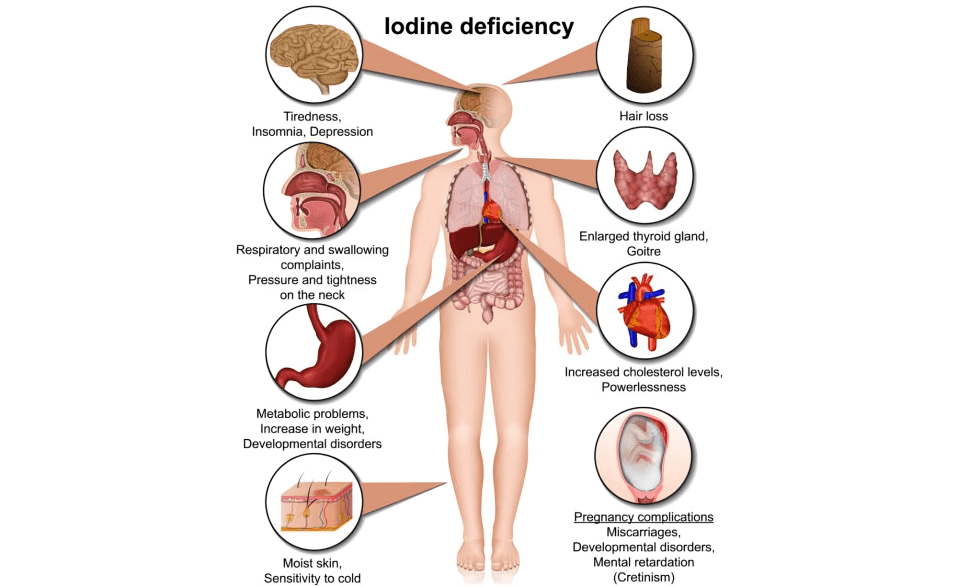
Iodine deficiency is one of the leading causes of thyroid disorders worldwide, particularly in areas where the diet lacks adequate iodine. This can lead to goiters, an enlargement of the thyroid gland.
People with thyroid disorders may experience hair loss or thinning. Hypothyroidism causes brittle hair; hyperthyroidism leads to shedding—both impact self-esteem and mental well-being. 5
The thyroid gland in the neck affects nearly every cell by regulating metabolism, heart function, digestion, and energy use, so disorders can broadly impact health and body functions. 6
A TSH blood test is the main diagnostic tool for thyroid disorders. High TSH indicates hypothyroidism; low TSH signals hyperthyroidism—helping doctors understand thyroid function and choose appropriate treatment.7
Pregnancy affects thyroid health due to increased hormone demands. Untreated thyroid disorders raise risks of complications such as preeclampsia, preterm birth, and developmental problems in the unborn baby.8
Thyroid disorders strongly affect bone health. Hypothyroidism causes brittle bones, while hyperthyroidism speeds up bone loss—both increasing the likelihood of osteoporosis and bone fractures over time. 9
Autoimmune thyroid disorders like Graves' disease or Hashimoto’s involve the immune system attacking the thyroid, leading to overactive or underactive function, which influences various areas of health.10
Thyroid disorders often disturb sleep. Hypothyroidism leads to fatigue and excessive sleepiness; hyperthyroidism causes insomnia—both disrupting sleep quality and daytime alertness.11
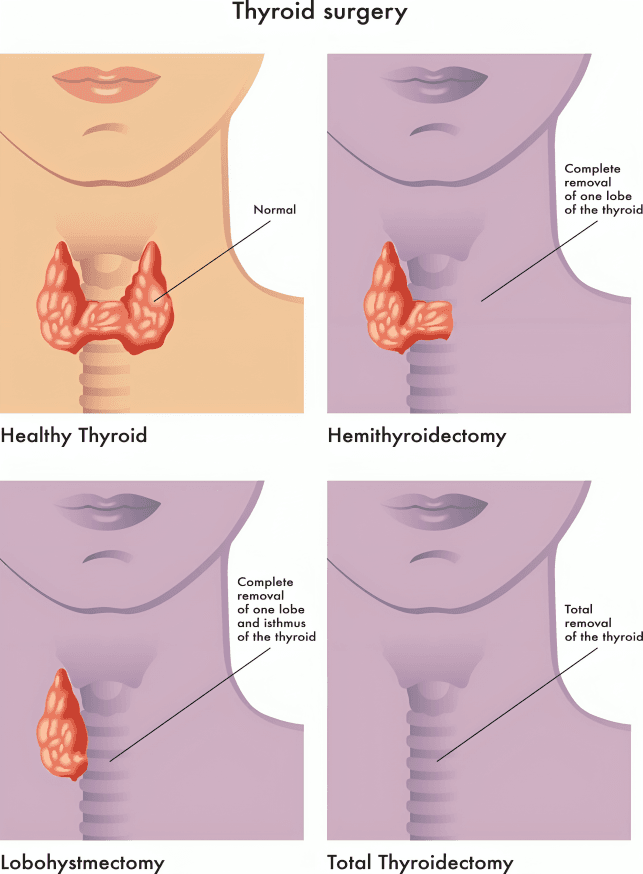
Surgery is sometimes required for thyroid disorders. Thyroidectomy, or thyroid removal, is done for thyroid cancer or severe hyperthyroidism that doesn't respond to other treatments.
Stress impacts thyroid health by altering hormone production. Chronic stress may trigger hormone imbalances, worsening existing disorders or contributing to new thyroid problems. 12
Regular monitoring is vital for thyroid disorder management. Blood tests track hormone levels and guide treatment since both excess and deficiency of thyroid hormones can cause serious health complications if left unmanaged. 13
Thyroid disorders affect skin health. Hypothyroidism causes dry, rough skin, while hyperthyroidism leads to thin, fragile skin—both increasing vulnerability to irritation, rashes, and infections due to impaired skin barrier function.14
A goiter, or thyroid gland enlargement, can accompany thyroid disorders. It may result from iodine deficiency or autoimmune conditions and often requires medical attention depending on size, symptoms, and underlying cause. 15
Thyroid disorders raise the risk of other conditions, including diabetes, high cholesterol, and high blood pressure. Maintaining proper thyroid hormone levels helps lower the chances of these related health issues.16
Thyroid function often declines with age, making thyroid disorders more frequent in older adults. Regular screenings help detect dysfunction early and support better health in later stages of life. 17


