“
The role of vaccinations in disease prevention is critical for safeguarding public health. Vaccines have been instrumental in reducing the spread of infectious diseases, protecting individuals and entire communities. This blog explores how vaccinations work, their effectiveness, and their role in maintaining global health. 1
1
”
Vaccines prevent serious diseases by training the immune system to fight infections, stopping illness before it starts, and protecting both individuals and communities. 1
Vaccination programs have drastically reduced or eradicated diseases like polio, measles, and smallpox, saving millions of lives and improving global public health. 2
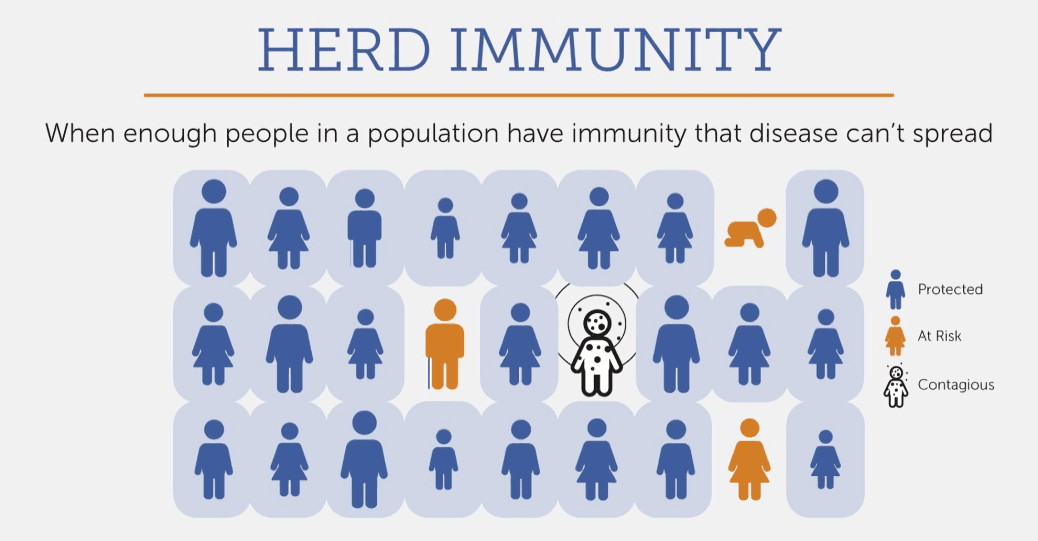
Immunization protects individuals and helps build herd immunity, slowing disease spread and safeguarding those who can't receive vaccines.
Childhood vaccinations, such as those for diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis, have reduced infant and child mortality rates, preventing long-term complications and saving countless lives globally.3
The global eradication of smallpox in 1980 is one of vaccination's greatest successes. Coordinated immunization efforts proved that vaccines can eliminate even the deadliest diseases.4
Vaccines help prevent the emergence of antibiotic-resistant diseases. By preventing diseases, they reduce the need for antibiotics, lowering the chances of resistance developing against these medications. 5
Vaccines save economies billions by reducing healthcare costs and lowering long-term treatment needs. Immunization programs save far more money than the cost of producing vaccines. 6
Vaccines have significantly reduced seasonal flu spread, leading to fewer hospitalizations, milder illness, and fewer flu-related deaths each year. Annual flu shots are recommended for most, especially seniors.7
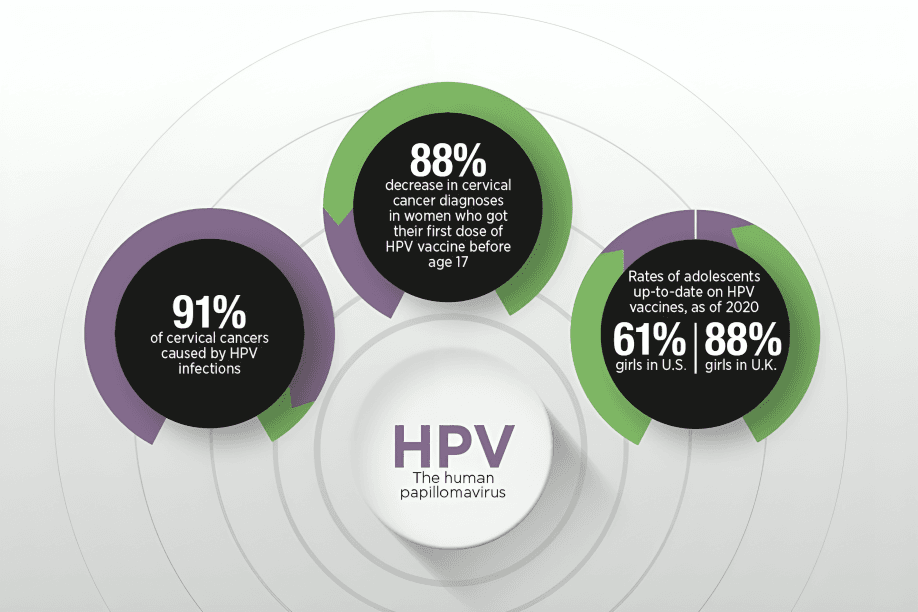
HPV vaccination has lowered the incidence of HPV-related cancers, including cervical cancer, and serves as a powerful cancer prevention tool, protecting future generations from this life-threatening virus.
Vaccines protect pregnant women and their unborn children from diseases like whooping cough and influenza. Immunization during pregnancy provides the baby with passive immunity, ensuring a level of protection at birth. 8
The rapid development and distribution of COVID-19 vaccines highlight advancements in vaccine technology. These vaccines have helped control virus spread, preventing severe illness and death during the pandemic.9
Vaccinations play a vital role in preventing disease outbreaks in schools and daycare centers. Keeping children vaccinated helps reduce absenteeism and ensures that learning continues without major disruptions.10
Vaccines like the tetanus shot offer long-term protection that can last for years. However, booster shots are important to keep immunity strong and provide continued defense against certain infections. 11
Vaccination has played a key role in protecting vulnerable populations, including the elderly and immunocompromised individuals, by reducing the overall burden of infectious diseases in the community. 12
Travel-related vaccinations are essential for individuals visiting areas with high disease risks, such as yellow fever, malaria, and typhoid. Immunization protects travelers from diseases common in certain regions.
Vaccination programs help close healthcare gaps by providing crucial immunizations to low-income and developing regions, leading to better global health and reduced disease spread. 13
The safety and effectiveness of vaccines are continuously monitored through clinical trials and surveillance, ensuring protection against evolving viruses and bacteria. 14
Pneumococcal vaccines have significantly reduced pneumonia cases worldwide, especially among children and older adults, making a major impact on respiratory health. 15
Vaccines improve quality of life by preventing serious illnesses, reducing the need for long-term treatments, and helping people live healthier, disease-free lives. 16
Immunization is one of the most fair and accessible health measures, often provided at little or no cost, reaching even the most underserved populations. 17


