
“
Vitamin D deficiency & its effects are often underestimated, yet they can significantly impact your overall health. This essential vitamin is vital for bone health, immune function, and more. When the body lacks enough Vitamin D, it can result in a variety of health issues. Understanding Vitamin D deficiency & its effects is crucial for preventing long-term complications. 1
1
”
Vitamin D deficiency can lead to weakened bones, as it plays a vital role in calcium absorption. Without adequate vitamin D, the body struggles to maintain bone density, increasing fracture risk. 1
Insufficient vitamin D is linked to an increased risk of osteoporosis, a condition where bones become brittle and fragile, heightening the chances of fractures. Proper vitamin D levels are essential for bone strength.2
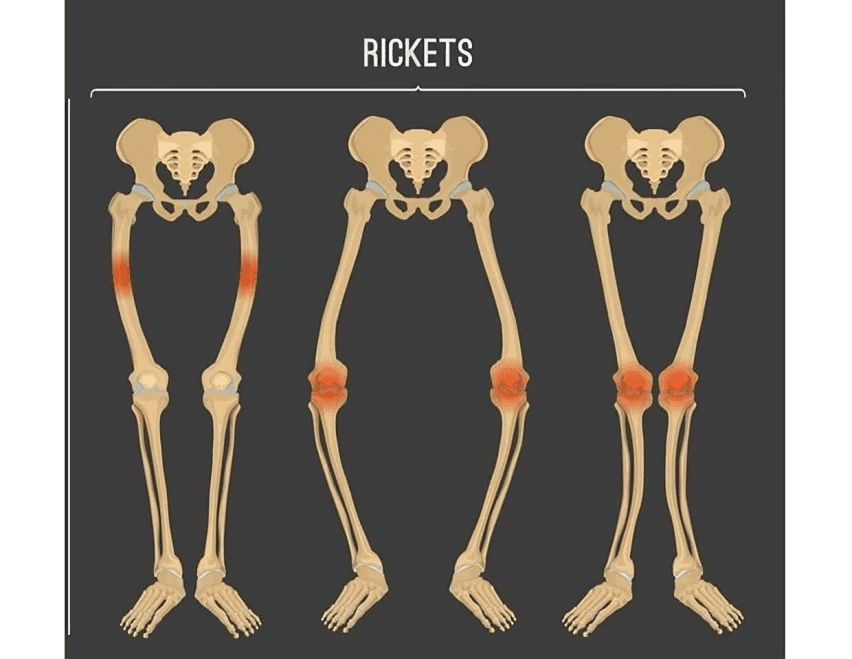
Children with vitamin D deficiency may develop rickets, a condition that causes weakened, bowed bones. Adequate vitamin D supports bone growth and prevents developmental issues.
Research suggests that vitamin D deficiency can contribute to muscle weakness, leading to an increased risk of falls, especially in older adults. Maintaining adequate levels helps preserve muscle strength. 3
Vitamin D plays a key role in immune function. Deficiency may impair the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections, including respiratory illnesses like colds, flu, and pneumonia. 4
Studies have found that low vitamin D levels are linked to an increased risk of depression. The vitamin plays a role in brain function, and a deficiency may contribute to mood disorders. 5
Chronic fatigue is another common symptom of vitamin D deficiency. As the vitamin is essential for energy production, insufficient levels can leave individuals feeling constantly tired and lethargic. 6
Insufficient vitamin D may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. It plays a role in regulating blood pressure, and a deficiency is linked to conditions such as hypertension and an increased risk of heart disease. 7
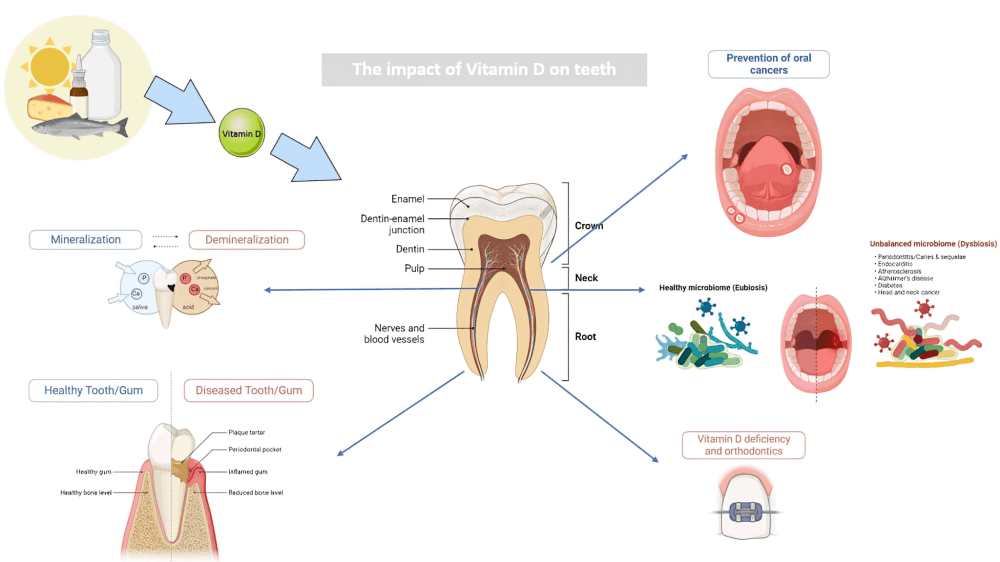
Vitamin D deficiency can lead to poor dental health. It is crucial for calcium absorption, and without it, teeth may become weak, leading to cavities, gum disease, and other dental problems.
Studies show that low vitamin D levels may increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, as the vitamin plays a crucial role in insulin production and blood sugar regulation, helping maintain normal levels. 8
Low vitamin D levels have been linked to an increased risk of certain cancers, including breast, prostate, and colorectal cancers. The vitamin supports cell growth and immune system regulation. 9
Individuals with vitamin D deficiency often experience chronic pain, especially in the muscles and joints. The vitamin helps regulate pain receptors, and a deficiency can lead to persistent discomfort and pain in these areas. 10
Vitamin D is essential for regulating calcium levels in the blood. A deficiency can lead to hypocalcemia, causing symptoms like muscle spasms, cramps, and tingling, particularly in the hands and feet. 11
Low vitamin D levels are associated with a higher risk of autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis (MS). The vitamin helps modulate immune system activity, which may reduce the likelihood of developing such conditions. 12
Vitamin D deficiency may contribute to weight gain or obesity by impacting the body’s ability to metabolize fat and regulate appetite, leading to an increased risk of weight gain and difficulty losing weight. 13
A lack of vitamin D can interfere with insulin regulation, making it harder for the body to process glucose properly. This disruption can increase the risk of insulin resistance and metabolic disorders. 14
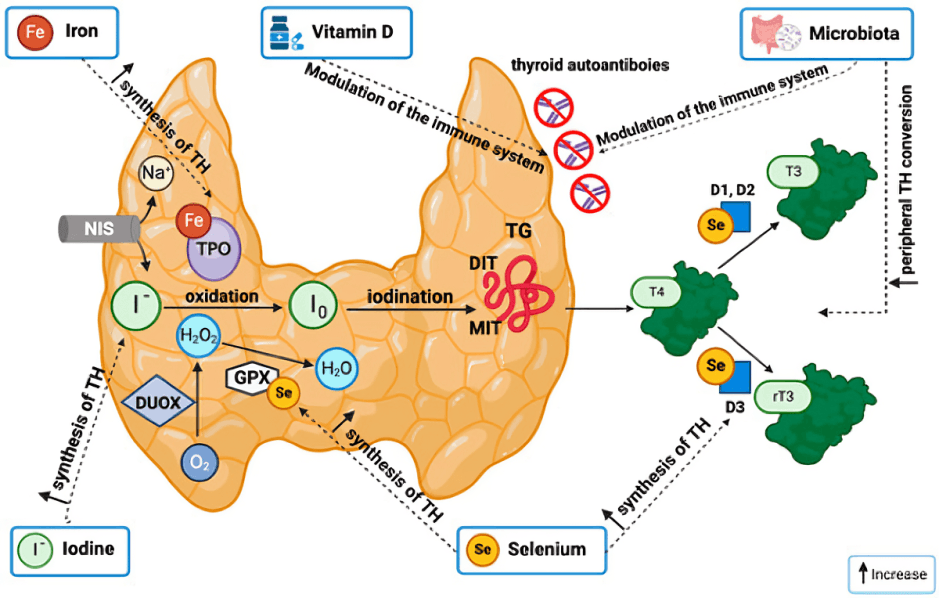
Vitamin D helps regulate the production of hormones crucial for healthy thyroid function. A deficiency can disrupt thyroid hormone regulation, potentially leading to issues like hypothyroidism.
Research suggests that low vitamin D levels may increase the risk of developing Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia. The vitamin is believed to protect brain health and cognitive function. 15
Pregnant women with vitamin D deficiency are at an increased risk of complications, including gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and premature birth. Adequate vitamin D is essential for both maternal and fetal health.16
Vitamin D deficiency can impair the body's ability to heal wounds. The vitamin is involved in the tissue repair process, and low levels can delay recovery from injuries, surgeries, and other types of trauma.17


