“
Muscles are a fascinating aspect of the human body. Driving our movements, supporting our posture, and enabling vital functions such as breathing and digestion. Understanding how muscles work can provide us with a deeper appreciation of our body's capabilities and the importance of maintaining muscle health. In this blog, we'll delve into 20 human muscle facts, each shedding light on the incredible ways they contribute to our daily lives.1
1
”
Muscles are classified into three types: smooth, cardiac, and skeletal. Smooth muscles operate involuntarily in organs like the gut and blood vessels. Cardiac muscles power the heart, while skeletal muscles attach to bones, enabling movement and daily activities. 1
The masseter, the strongest muscle in the human body, is crucial for chewing. Located in the jaw, it can exert a remarkable force of up to 250 pounds. This incredible strength highlights its essential role in breaking down food during digestion. 2
The largest muscle in the human body is the gluteus maximus, found in the buttocks. It plays a key role in extending the hip joint, which is essential for activities like walking, running, and climbing stairs, providing strength and mobility. 3
Your body has over 600 muscles, including those in your arms, legs, and vital organs like the heart. These muscles work alongside 206 bones, enabling movement, maintaining your heartbeat, and aiding in digestion. 4
Muscle cramps are sudden, involuntary contractions of muscles. They can occur due to dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, or overuse. These cramps often cause pain and discomfort, highlighting the need for proper hydration and balanced electrolytes to prevent them. 5
Muscles consist of specialized cells called muscle fibers, which possess contractibility—the ability to shorten or lengthen. This contractibility is essential for nearly all body movements, enabling actions like walking, lifting, and even the heartbeat. 6
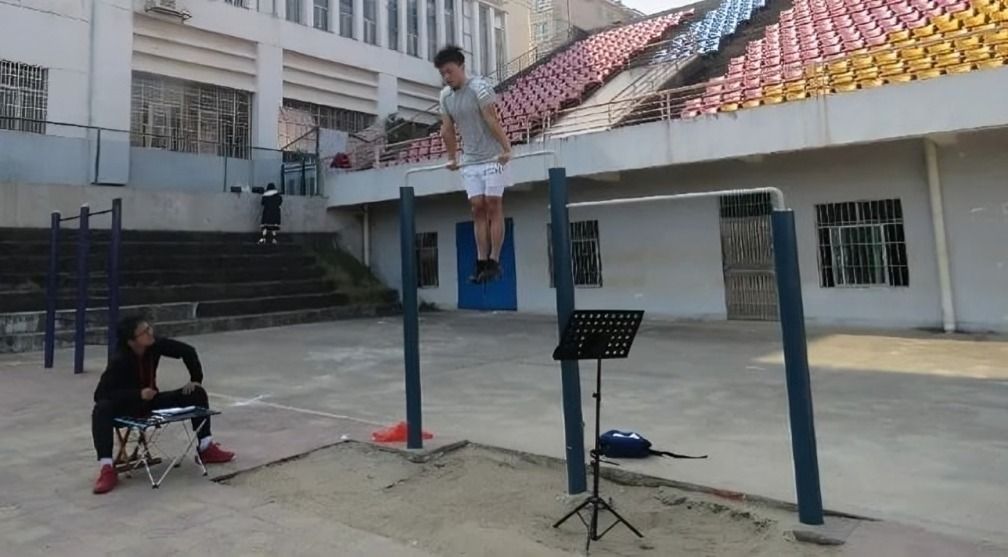

Xiao Lin from China set the record for the most muscle-ups in one hour, achieving 402 on November 28, 2021, at Ji'an Sports Centre in Jiangxi. A university student and fitness enthusiast, Lin demonstrated extraordinary strength and endurance.
The smallest muscles in the body are located in the inner ear and include the tensor tympani and stapedius. These muscles connect to the eardrum and help stabilize the inner ear. Additionally, the smallest bones, known as ossicles, are found in the ear. 7
A cheetah's muscles can contract at incredible speeds, enabling it to reach speeds up to 75 mph in just a few seconds. Its specialized muscle fibers allow for rapid acceleration and extraordinary sprinting capability. 8
Muscle disorders include conditions like muscular dystrophy, myasthenia gravis, and fibromyalgia. These disorders can lead to muscle weakness, pain, and fatigue, significantly impacting a person's mobility and quality of life. 9
In the human body, muscles typically make up about 40% of body weight in men and around 35% in women. This percentage reflects the crucial role muscles play in overall body composition and physical strength.10
The eye muscles are estimated to move over 100,000 times a day, with many of these movements occurring during the dreaming phase of sleep. This high frequency of movement is crucial for visual processing and dream activity. 11
The heart is the hardest-working muscle in the body, pumping approximately 2,500 gallons of blood daily. Its continuous, powerful contractions sustain circulation and supply vital nutrients and oxygen throughout the entire body. 12
Most body heat is generated through muscle contraction, accounting for about 85% of the total heat produced. When you're cold, muscles contract involuntarily, and shivering occurs as muscles work to generate warmth and regulate your body temperature. 13
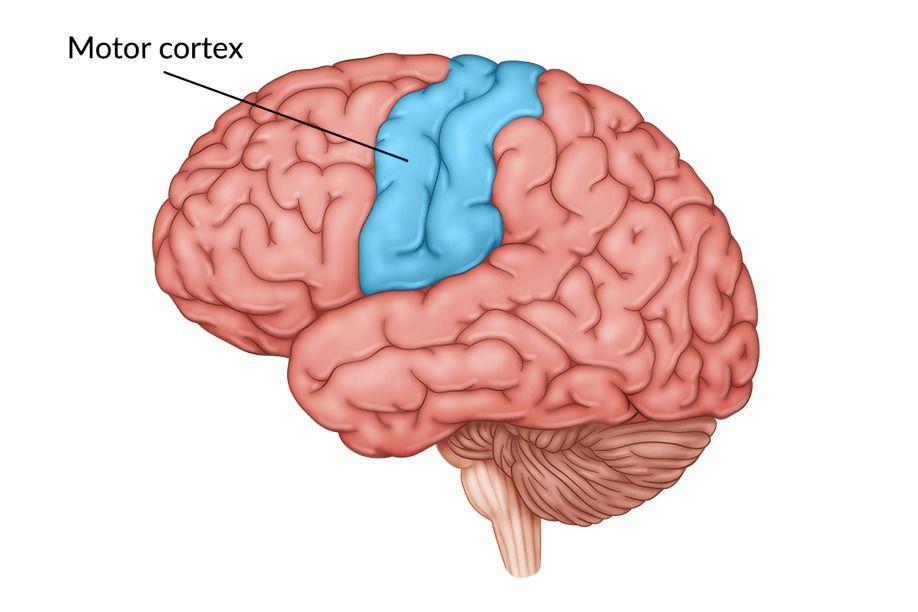
The motor cortex in one side of the brain controls muscle movement on the opposite side of the body. For example, the right cortex manages the left side's muscles. Complex movements, like shooting a basketball, involve more intricate brain signals.
Muscle stimulators, which use electrical currents to induce muscle contraction, have treated muscle weakness and atrophy for decades. Recent advancements in technology have produced more sophisticated and effective devices, enhancing their treatment capabilities and outcomes. 14
The first documented treatment for muscle injuries dates back to ancient Greece. Around 400 BCE, Hippocrates, often called the father of medicine, described methods for treating muscle strains and injuries, using techniques such as rest and manual therapy to aid recovery. 15
Muscles can only pull, not push. When pushing a door, your muscles are actually pulling your elbow and shoulder against it. Muscles contract to pull bones, while paired antagonistic muscles pull the bone back to its starting position. 16
Muscles have a rich blood supply, which accelerates their healing process compared to other tissues like bone or tendon. This enhanced circulation helps muscles recover more quickly from injuries and stress than less vascularized tissues. 17
Walking, though it seems simple, involves the coordination of over 200 muscles. This complexity makes it challenging for newborns to master and difficult for individuals recovering from conditions like stroke to retrain their walking ability effectively. 18


