“
In this blog, we’ll delve into the fascinating functionality of heels and their critical role in our everyday lives. Heels are integral to supporting our body weight, maintaining balance, and absorbing shock during activities like walking and running. They are connected to our calf muscles by the strong Achilles tendon, which enables powerful movements such as jumping and sprinting. The evolution of heels has been pivotal in helping us walk on two legs, a key feature that sets us apart from other animals. From sports to daily routines, heels are essential for both mobility and stability. As we age, taking good care of our heels becomes increasingly important to ensure comfort, prevent injuries, and support overall foot health. Understanding the significance of heels can help us appreciate their role and maintain their health throughout our lives.1
1
”
The calcaneus, or heel bone, is the largest bone in your foot. Its strong and sturdy structure supports the entire body's weight, acting as a crucial foundation for movement. This robust shape enables the heel to absorb shock. 1
The heel fat pad, a thick cushion beneath the heel, acts as a shock absorber, dispersing the impact forces generated during walking or running. This vital layer helps to minimize injury risk by protecting the bones and soft tissues of the foot. 2
Treatments for heel pain, like plantar fasciitis, often involve exercises, orthotics, and injections to reduce inflammation and enhance comfort. These approaches help alleviate pain and support recovery, ensuring better foot health and function.3
The roughened area known as the tuber calcanei, located on the back of the heel bone, supports a significant portion of the body's weight when standing. This structure provides essential stability and balance.4
The Achilles tendon, the largest and strongest tendon in the body, attaches at the back of your heel. It plays a crucial role in enabling movement, such as walking, running, and jumping, by connecting the calf muscles to the heel. 5
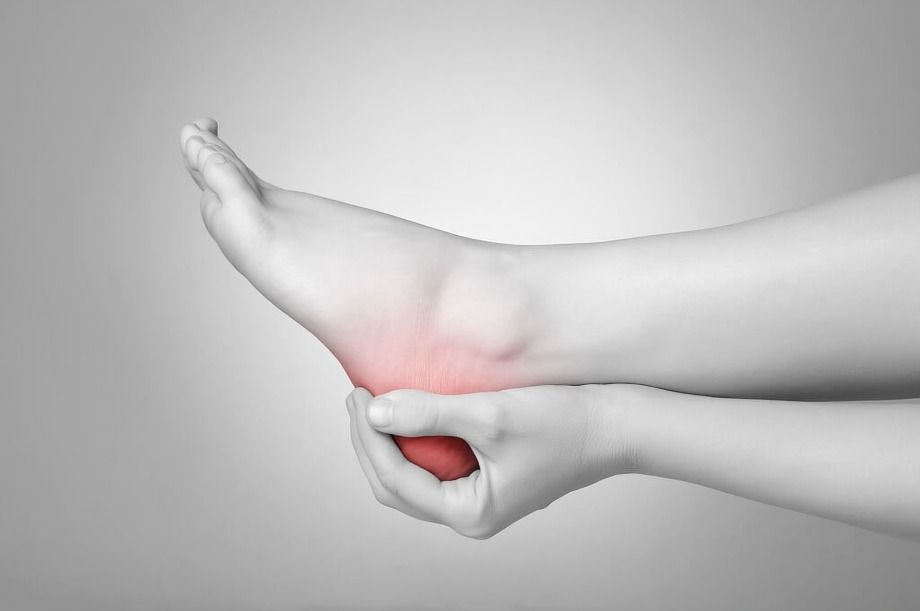
Heel bruises can be very painful, often resulting from hard impacts or injuries. When the heel experiences a sudden blow or significant force, it can become sore and tender. This discomfort can make walking or standing quite painful and challenging.
Like humans, animals like raccoons and bears walk with their heels touching the ground. In contrast, animals such as horses, dogs, and cats walk on their toes, showing the diversity in locomotion among mammals. 6
Over time, calcium deposits may build up on the underside of the heel bone, leading to the formation of heel spurs. These bony growths can be quite painful and are frequently linked to conditions such as plantar fasciitis. 7
Although the heel bone is robust, it can fracture under extreme stress, such as from a high-impact injury or fall. These fractures are often very painful and may require medical treatment to properly heal and restore full function. 8
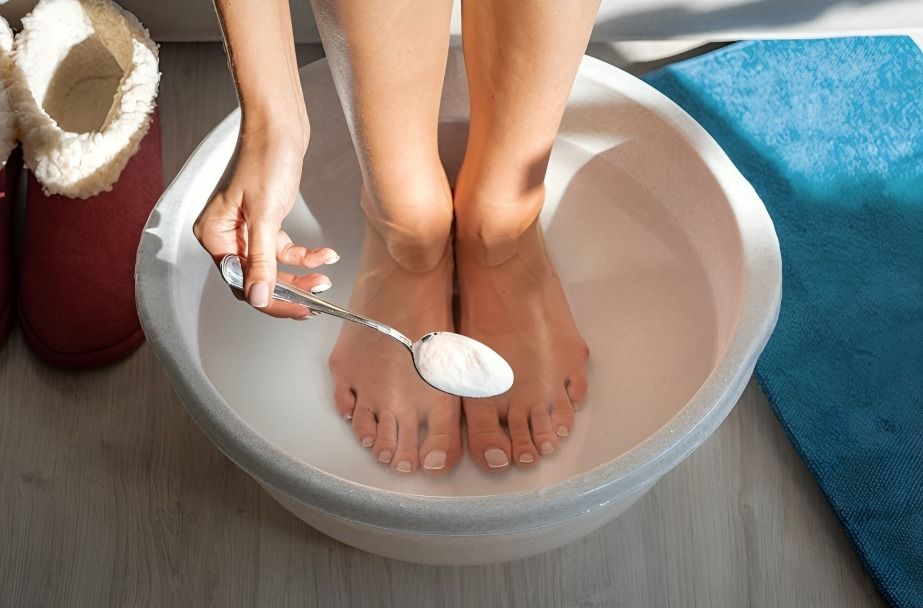

Maintaining proper foot and heel hygiene is crucial for preventing infections, odors, and other foot issues. This involves regularly washing your feet, controlling moisture, and wearing clean socks and shoes.
Unique to humans, the lateral process is a small bump on the heel bone that aids in maintaining balance while standing upright. This feature is crucial for our bipedal posture, providing stability and support during walking and standing. 9
Modern athletic shoes frequently include advanced heel cushioning technologies, such as gel inserts or air pockets. These innovations are designed to minimize impact and maximize comfort during physical activities. 10
Overpronation or underpronation of the heel can affect gait and lead to various foot and ankle problems. Proper footwear and orthotics can help correct these issues. While in Overpronation, the foot doesn’t roll inward enough. 11
The calcaneus grows rapidly during childhood and adolescence, reaching full size by around age 15-16, playing a crucial role in the overall development of the foot. Proper development of the calcaneus is crucial for overall foot function and stability. 12
Historical evidence reveals that ancient Egyptian sandals were designed to protect the heel, highlighting the early recognition of heel protection for comfort and durability. This shows how important heel care was even thousands of years ago.13


