“
Mesolithic art stands as one of the most profound testaments to early human creativity, bridging the gap between the Paleolithic and Neolithic periods. This article explores 20 Fascinating Facts about Mesolithic Art and the culture they reveal.1
1
”
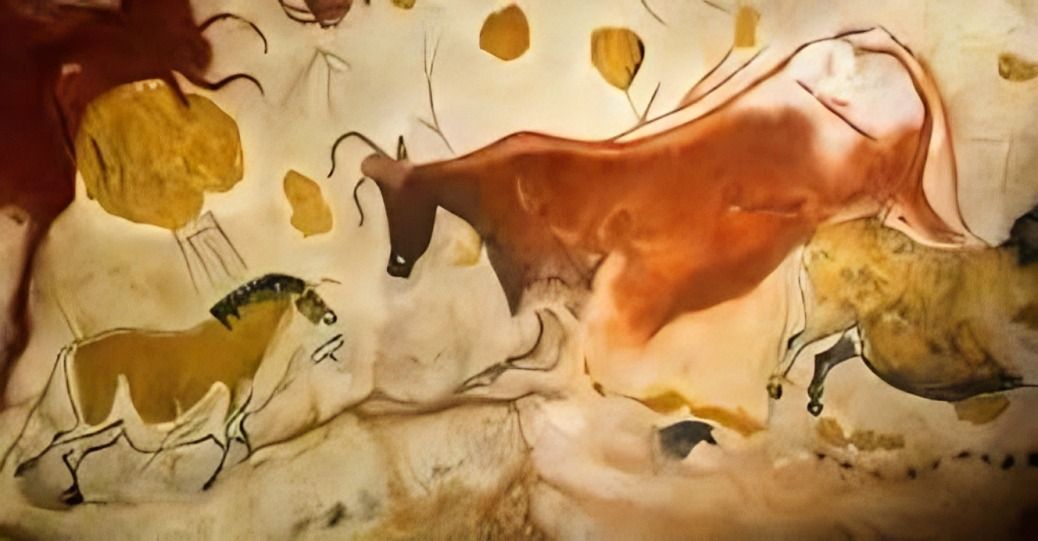
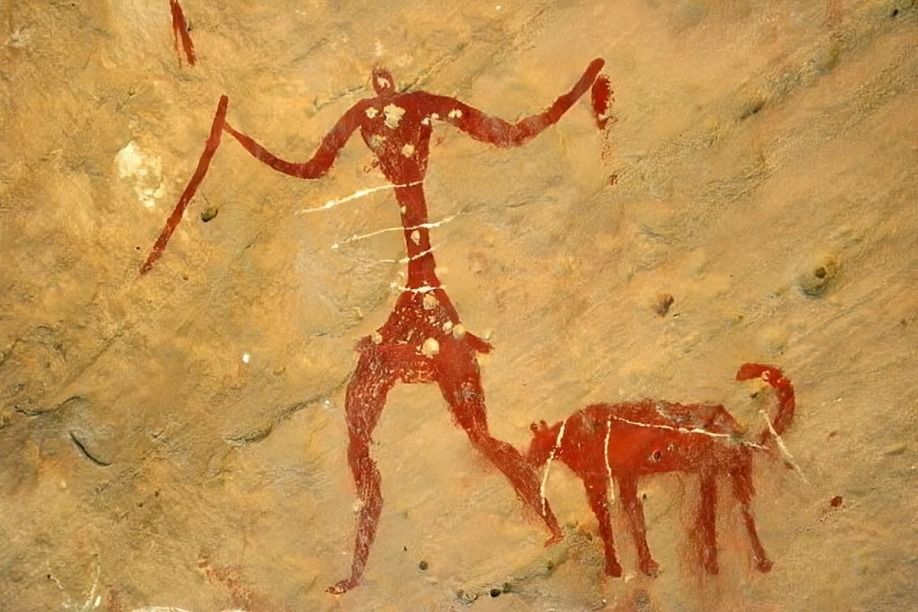
Several remarkable Mesolithic rock art sites can be found along the Mediterranean coast of Spain. This art features small painted figures of humans and animals.
The human figure frequently takes center stage in these painted scenes, highlighting the importance of human activities in Mesolithic life. 1
In addition to hunting, the rock art also depicts scenes of battle and dancing, reflecting the social and cultural practices of Mesolithic communities. 2
One of the most fascinating aspects of these artworks is the representation of honey gathering, especially at Cuevas de la Araña in Bicorp. 3
Overall, the rock art of the Mediterranean coast of Spain serves as a rich historical record of human activity during the Mesolithic era. 4

The painting known as The Dancers of Cogul is an excellent example of how movement can be conveyed in static art. This scene features nine women, a novel representation for the region, some painted in black and others in red.
In addition to the human figures, the artwork also includes several animals, notably a dead deer or buck that appears to be impaled by an arrow or atlatl. 5
The term "Mesolithic art" encompasses all forms of art and crafts produced between the conclusion of the Paleolithic Ice Age around 10,000 BCE and the advent of farming, which includes agriculture and animal husbandry. 6
The duration of the Mesolithic period varied by region, depending on how quickly agriculture was established. This era marks the beginning of the Holocene epoch, succeeding the Pleistocene, and introduces a shift in Stone Age art. 7
Mesolithic rock art features a variety of subjects, including animals like deer and horses, reflecting the daily life and hunting practices of these early humans. 8
These artworks are found in several locations across Europe, particularly in regions such as Spain, France, and Scandinavia, showcasing widespread cultural practices. 9

Many petroglyphs include abstract symbols, believed to have held religious or ritual significance, serving as a means of communication or expression of beliefs.
Artists used natural pigments from minerals and plants, including ochre and charcoal, to create vibrant colors that have remarkably survived over millennia. 10
Mesolithic art techniques varied; some used stencils made from hands or animal skins, while others involved direct painting or carving into rock surfaces. 11
The depictions suggest motion, with animals painted to imply running or jumping, indicating an understanding of animal behavior related to hunting. 12
While some Mesolithic art is found in caves, many petroglyphs are located in open-air sites, revealing different contexts for artistic expression. 13
Some researchers suggest that certain symbols and figures may represent shamanistic practices, reflecting the spiritual beliefs of these early peoples. 14
Many rock paintings and petroglyphs date back to around 10,000 to 5,000 BCE, placing them in a transitional period between hunter-gatherer societies and settled agricultural communities. 15
Certain animals, like the aurochs and reindeer, frequently appear in Mesolithic art, possibly symbolizing important aspects of the community’s livelihood. 16
Archaeological studies of Mesolithic rock art provide insights into the cognitive and social development of early humans, illustrating their capacity for abstract thought. 17